Amines
return
The most important of the organic
compounds showing appreciable basicity.
The amines are the organic
bases.
Nomenclature
Aliphatic amines are named by naming the alkyl group
followed by the word -amine.
Complicated amines are named by prefixing amino- to the name
of the parent chain.
Aromatic amines are named as derivative of the simplest
aromatic amine, aniline.
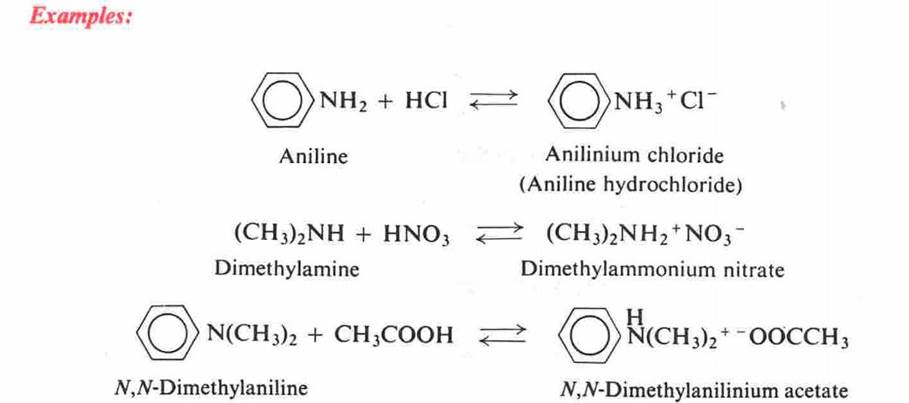
Salts of amines are named by replacing -amine by -ammonium
(or -aniline by -anilinium).
Physical Properties
Polar compounds
Form intermolecular hydrogen bonds
Higher boiling points than nonpolar compounds
Lower boiling points than alcohols or carboxylic acids
Quite soluble in water
Methyl amines & ethyl amines smell like ammonia
Higher alkyl amines have a fishy smell
Aromatic amines are generally very toxic; they are absorbed
through the skin, often with fatal results
Aromatic amines are oxidized by air
Stereochemistry of Nitrogen
Nitrogen uses sp3 hybridized orbitals
Tetrahedral shape
one orbital is a pair of
nonbonding electrons
the three remaining orbitals
overlap s orbitals of hydrogen or carbon
Approximate bond angles of 109o
Quaternary ammonium salts use all four sp3 orbitals
to form bonds
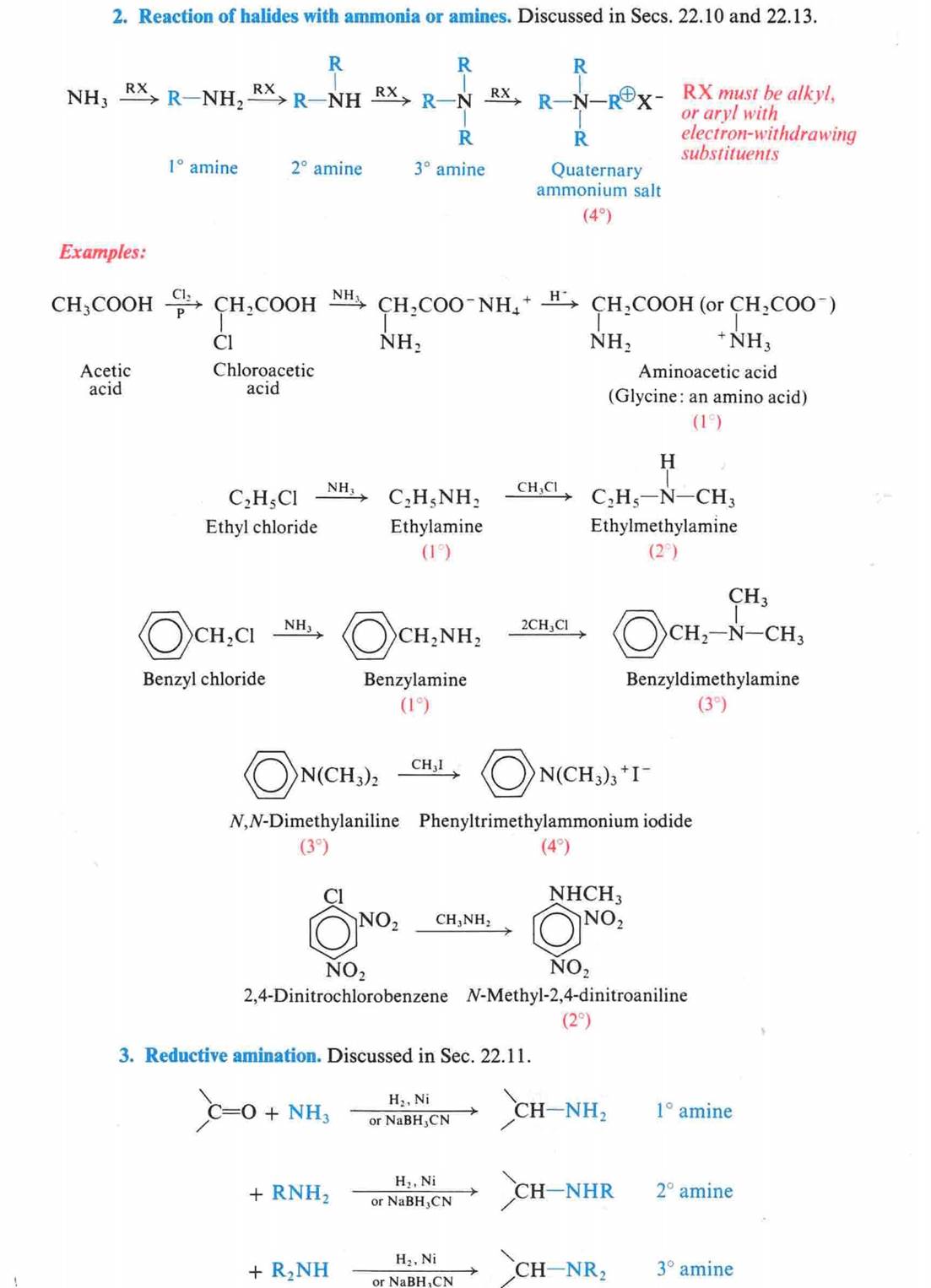
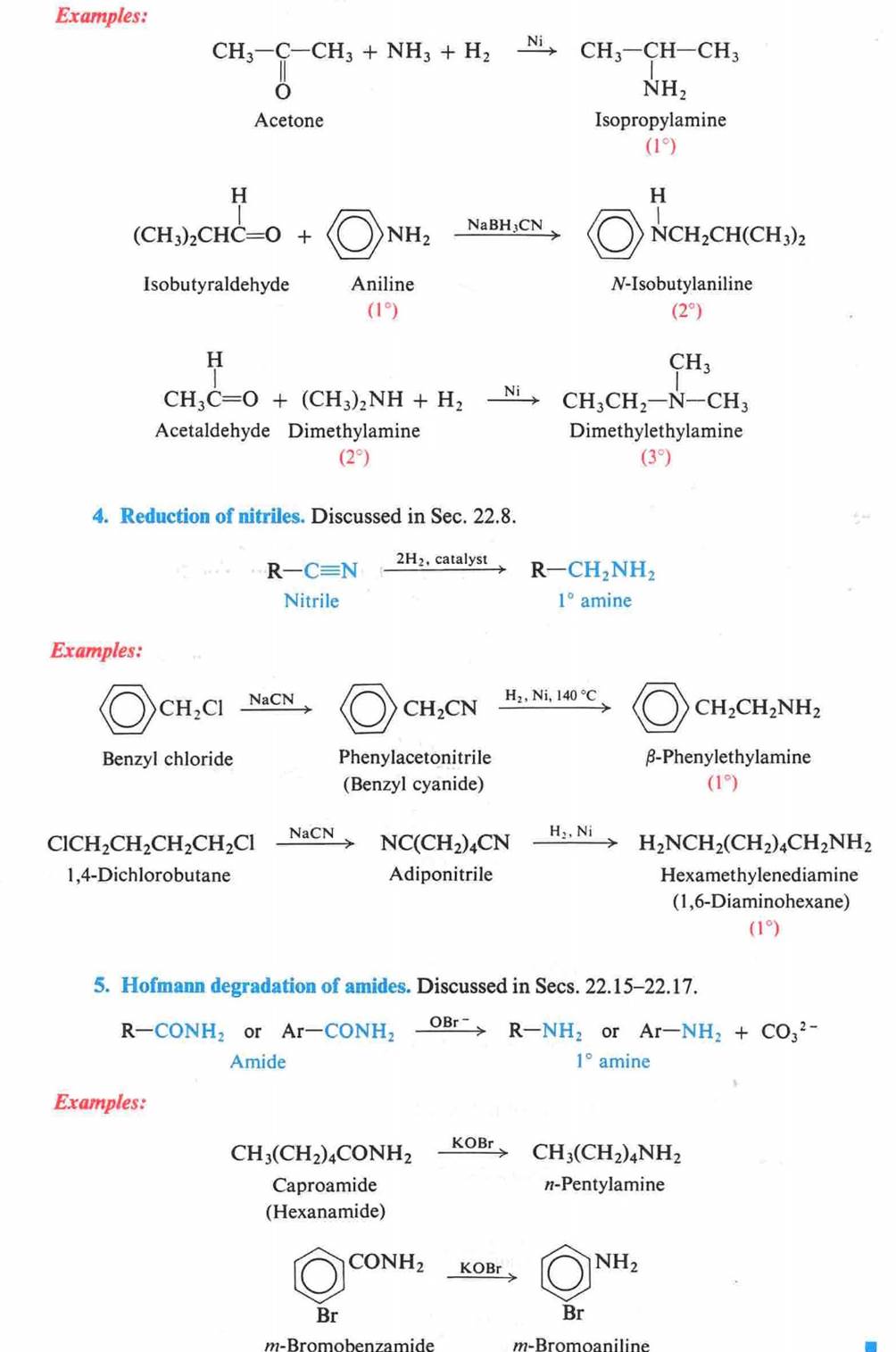
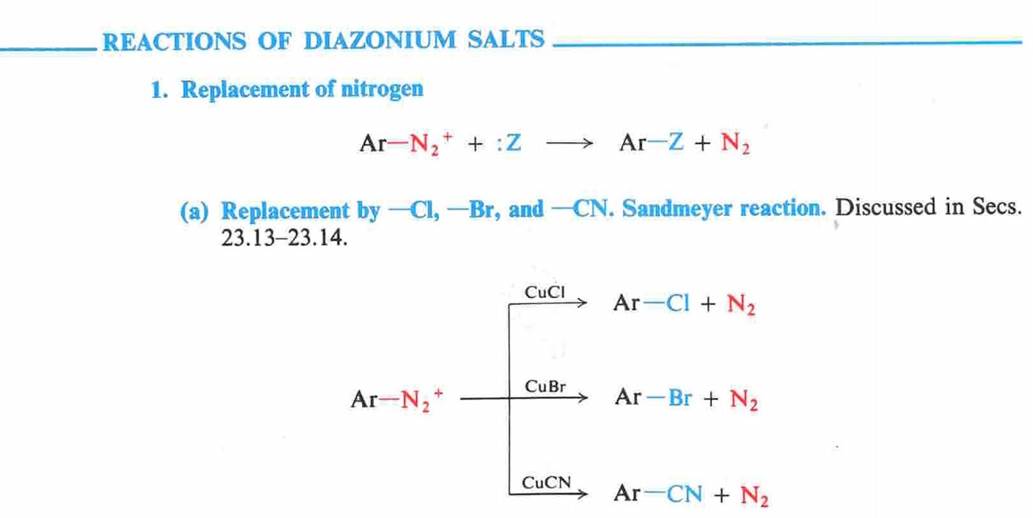
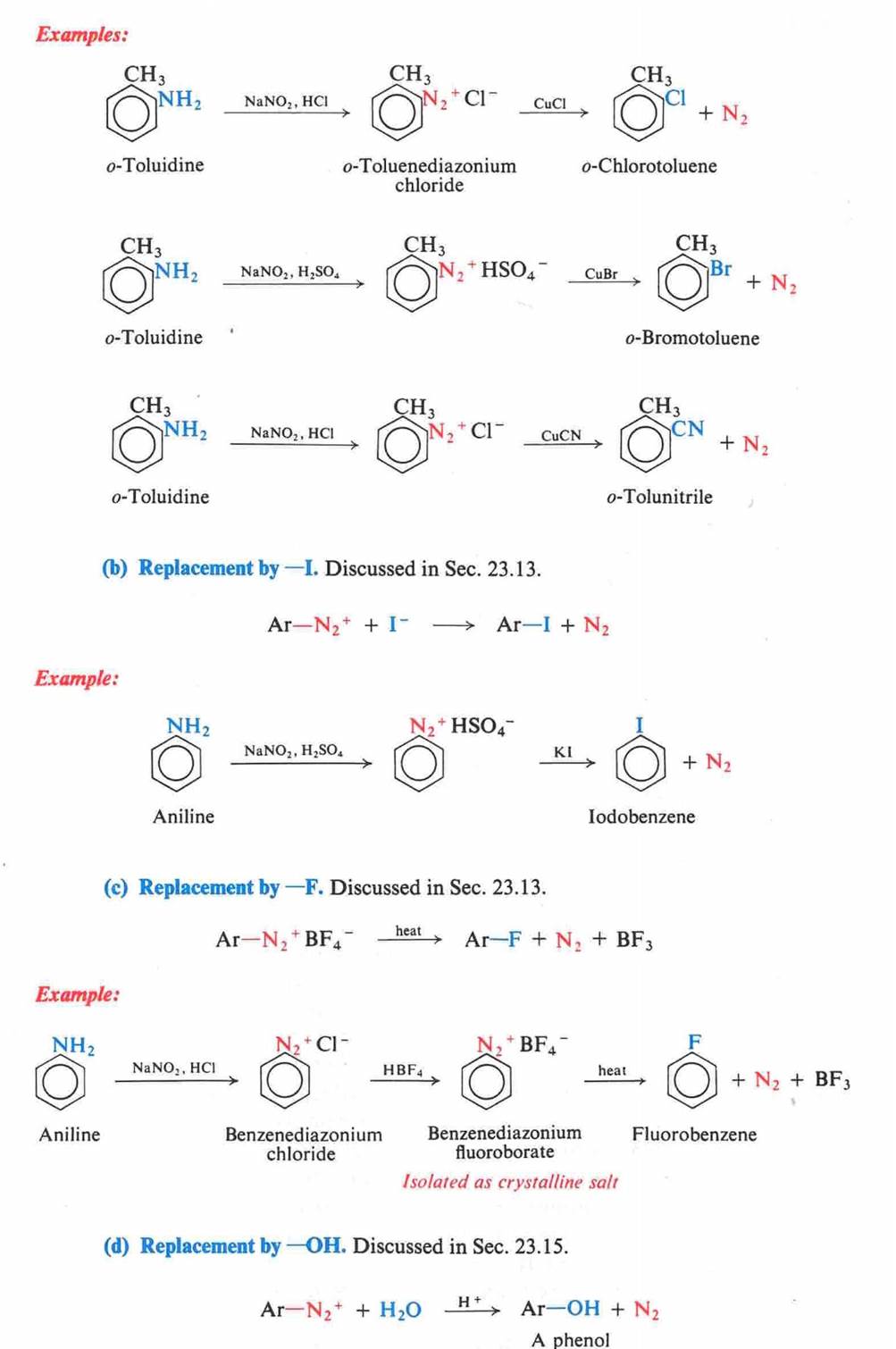
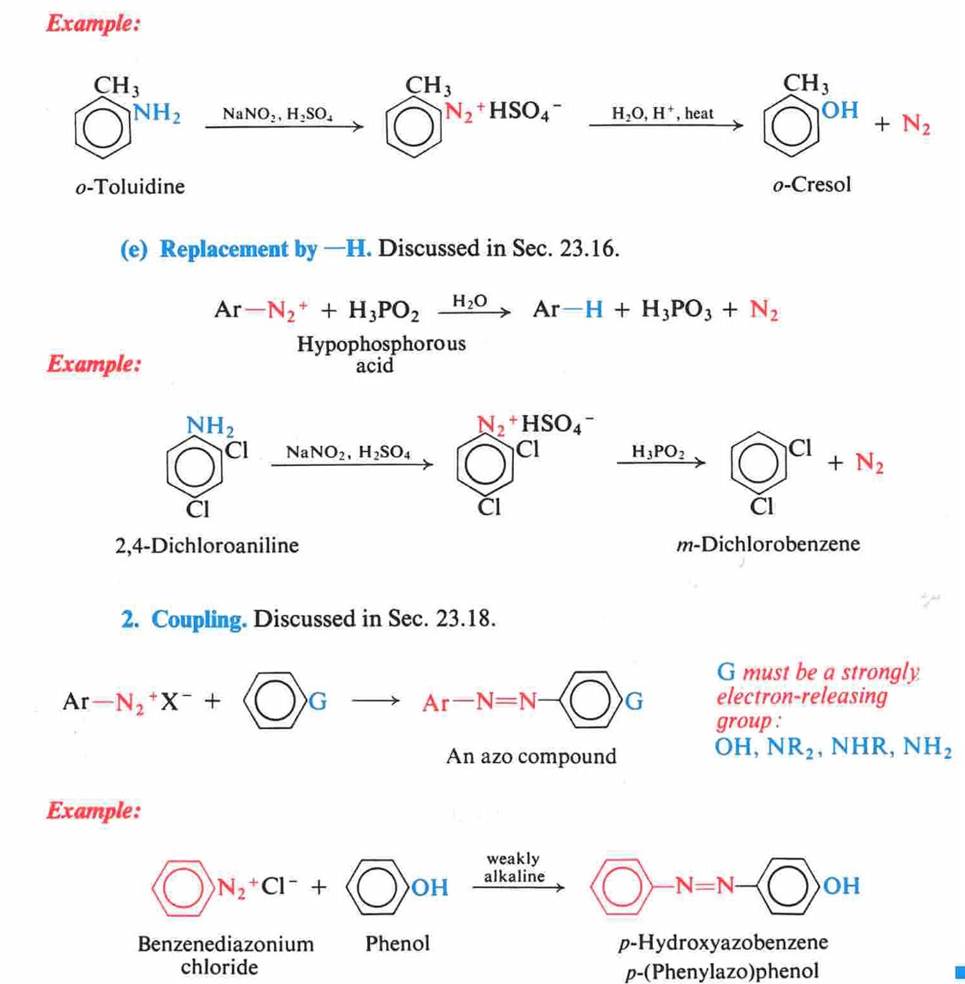
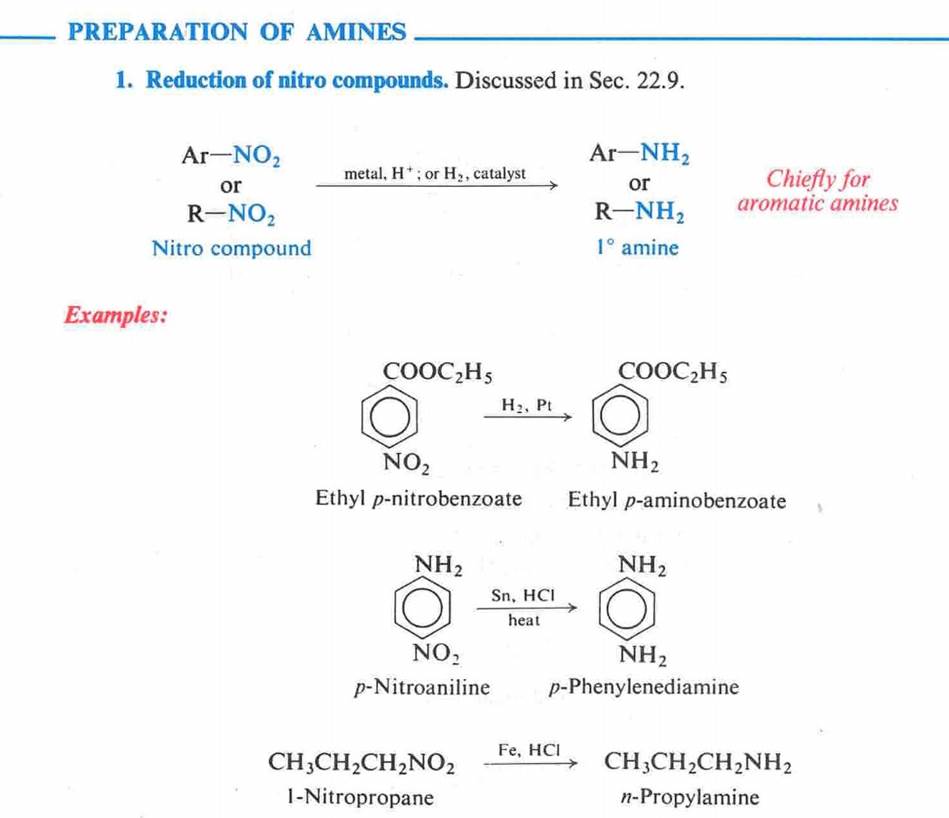
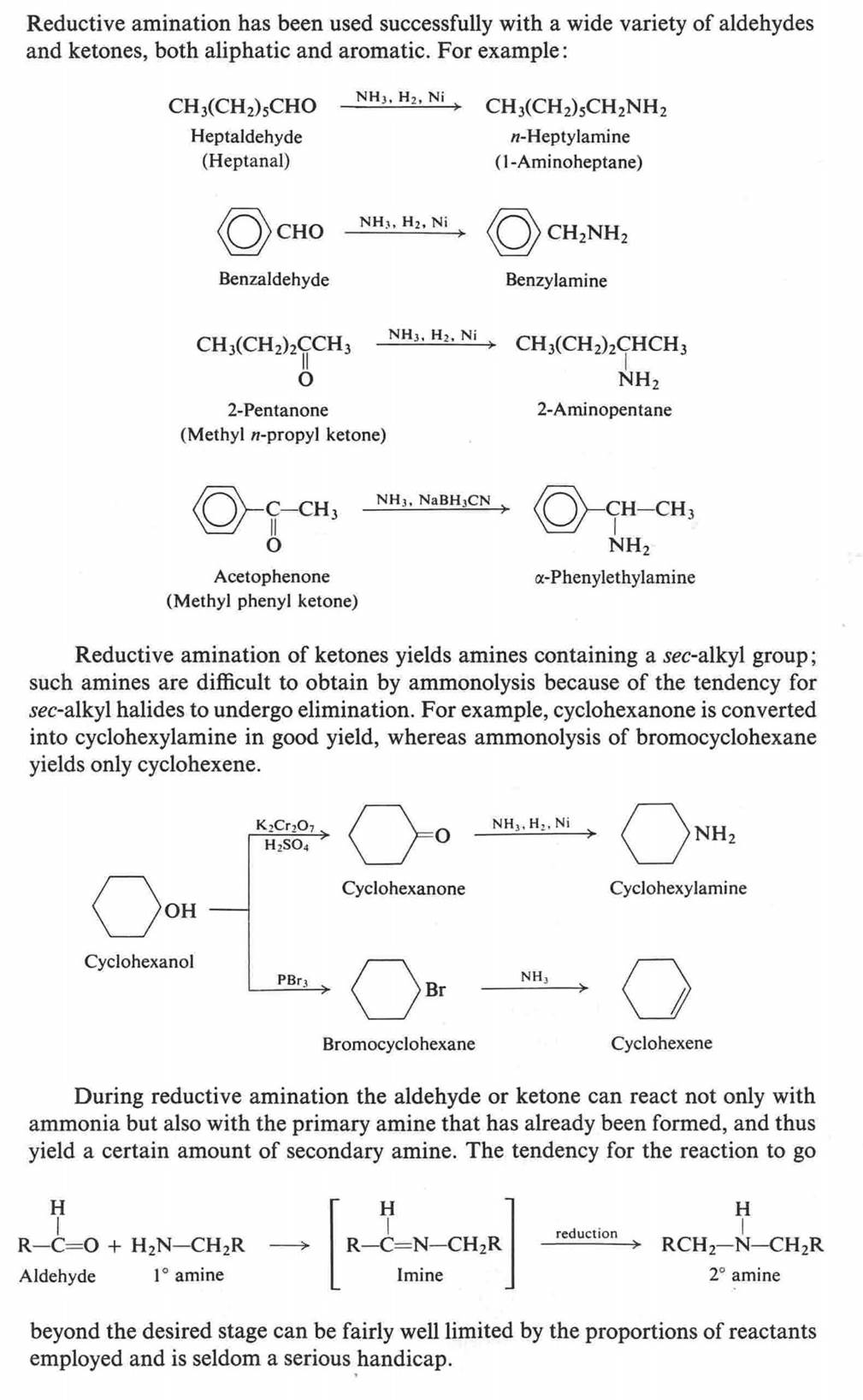
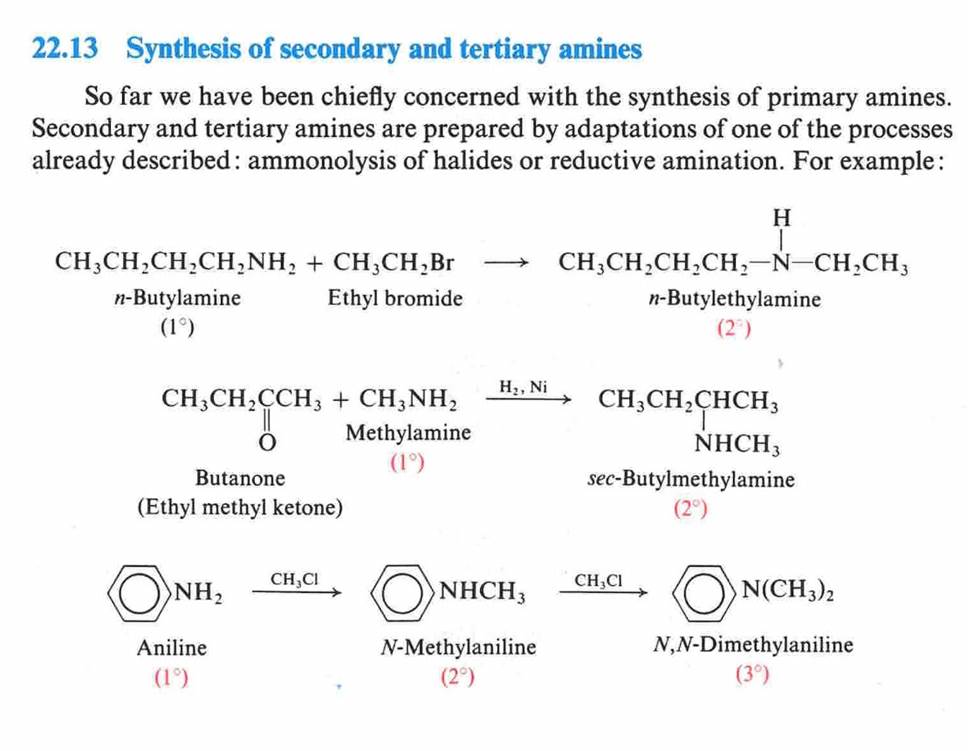
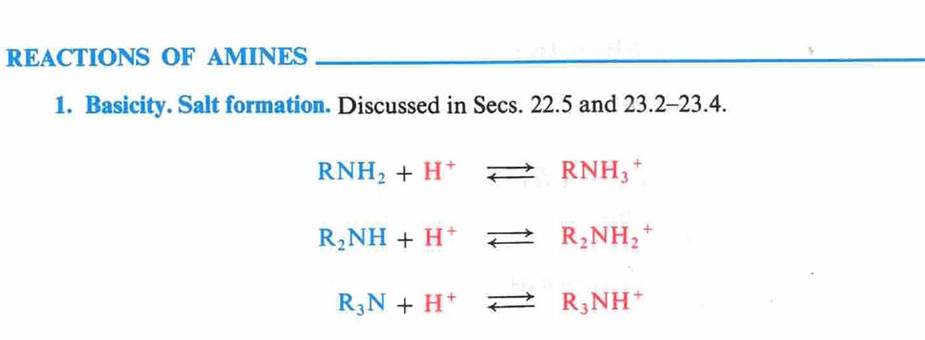
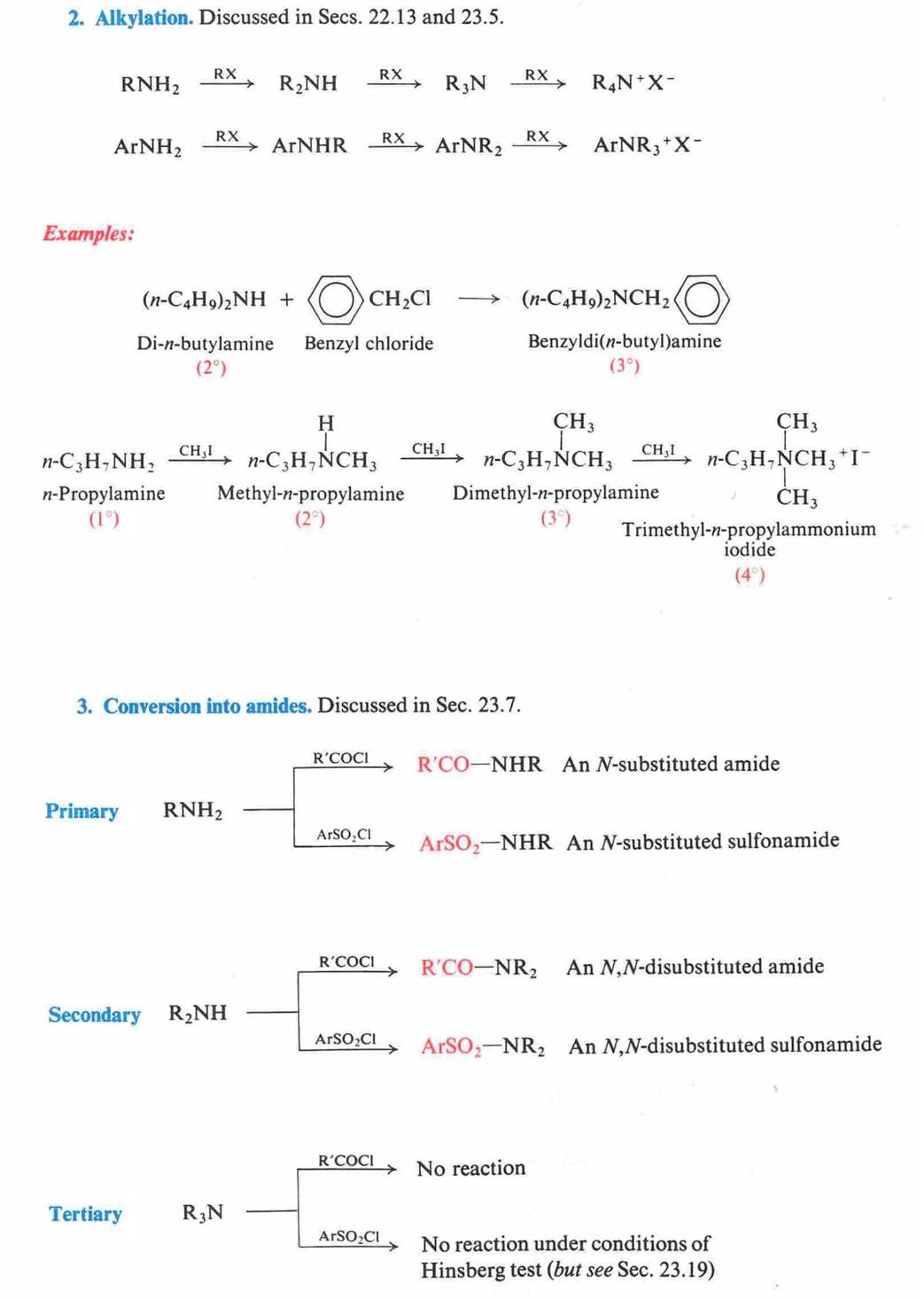
Hofmann Degradation of
Amines
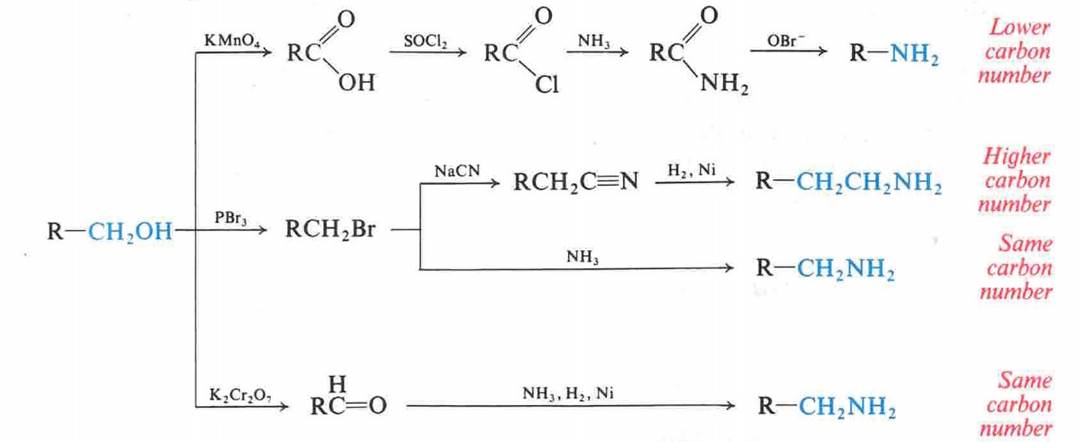
![]()
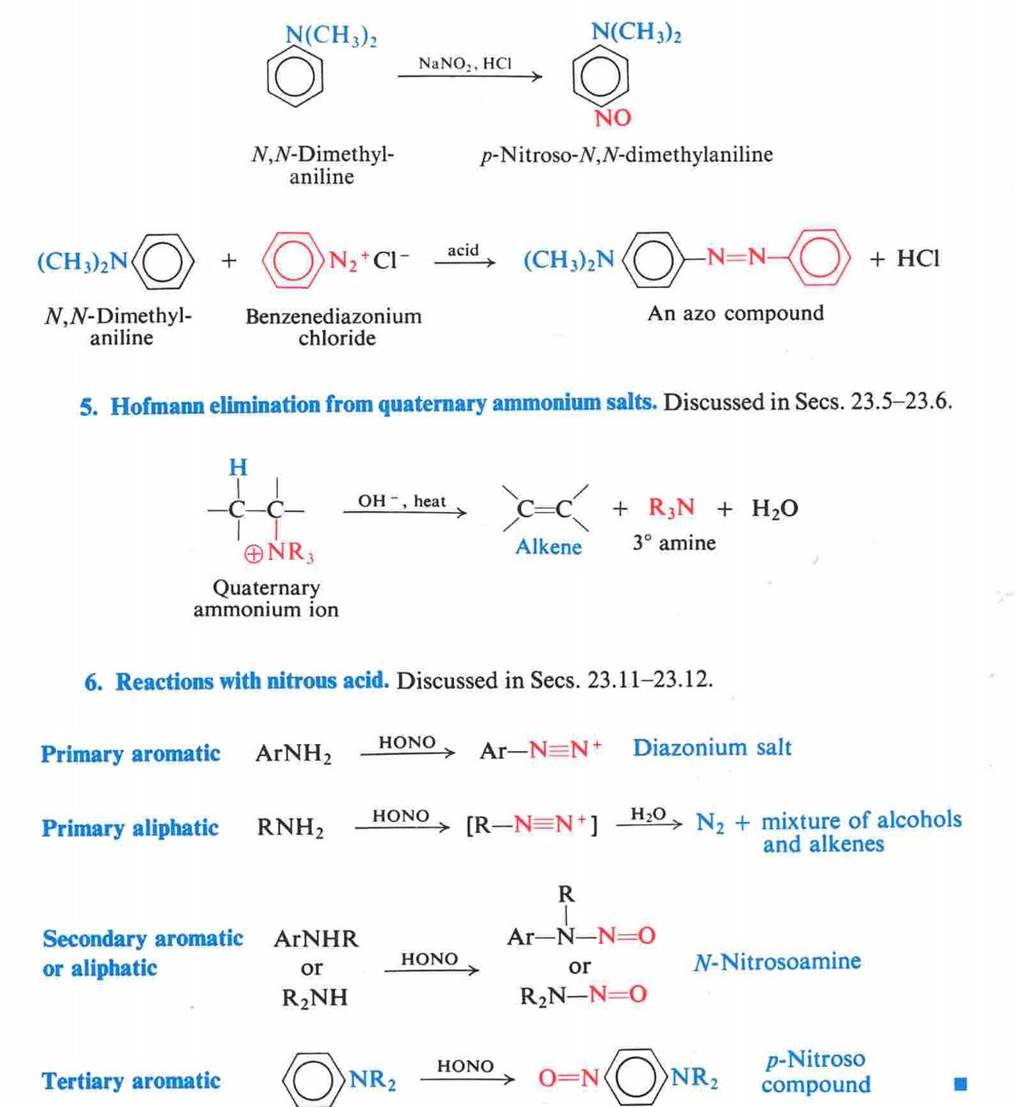
When a primary aromatic amine,
dissolved or suspended in cold aqueous mineral acid,
is treated with sodium nitrite, a
diazonium salt is formed.