Aldehydes & Ketones
Carbonyl Compounds: The carbonyl group determines the chemistry
of
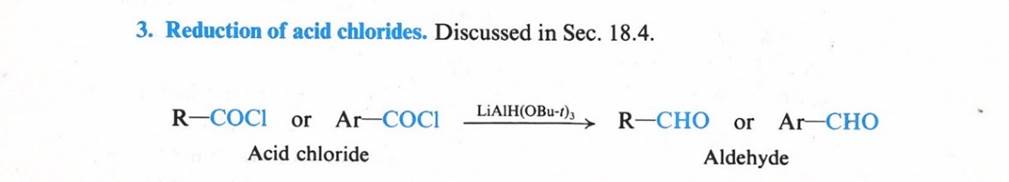
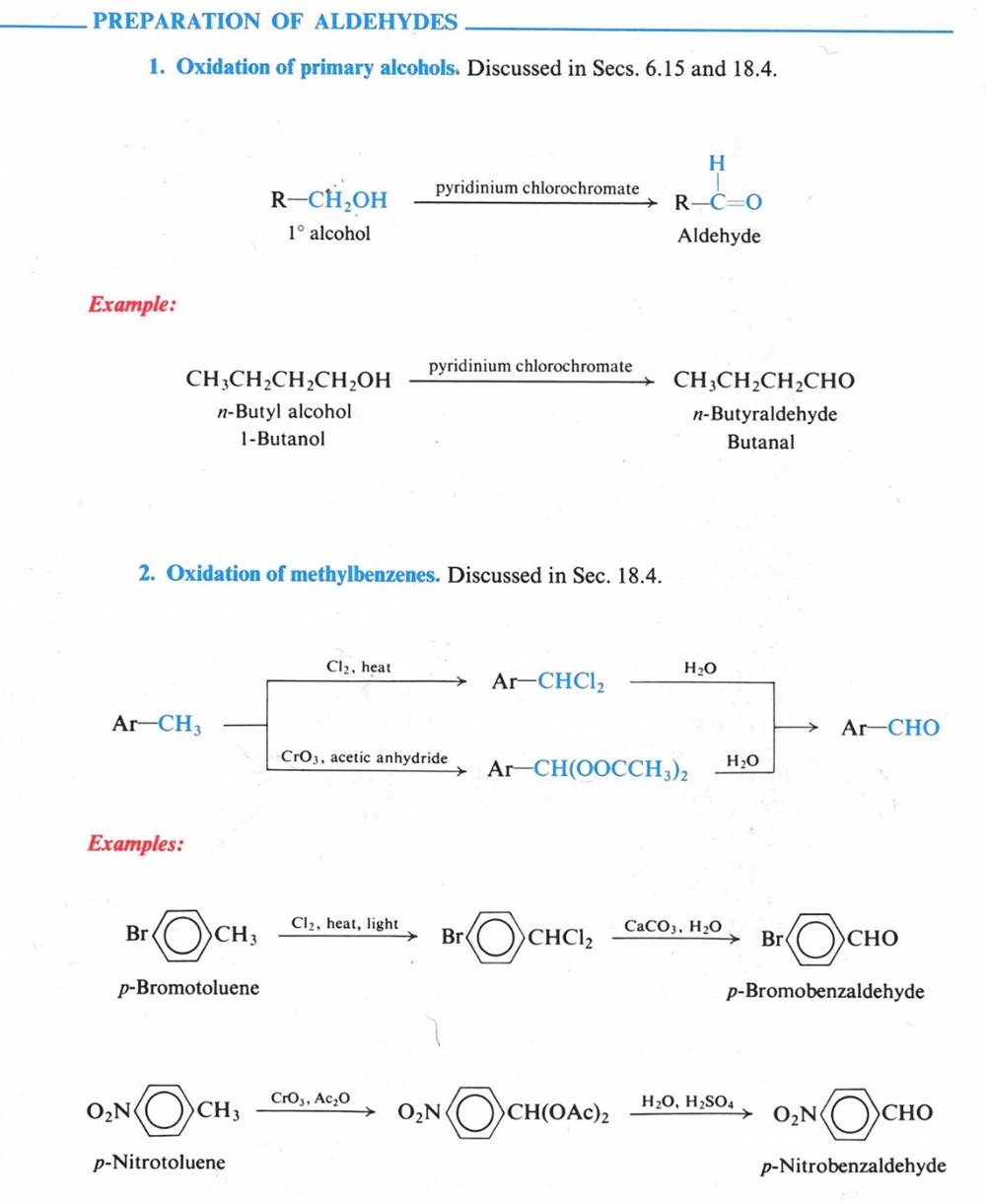
aldehydes & ketones
A flat
molecule due to sp2 hybridization
Aldehydes
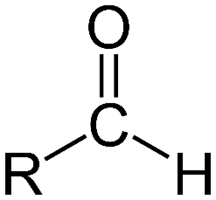
Ketones
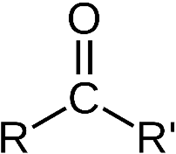
Aldehydes
& Ketones resemble each other closely in most of their properties.
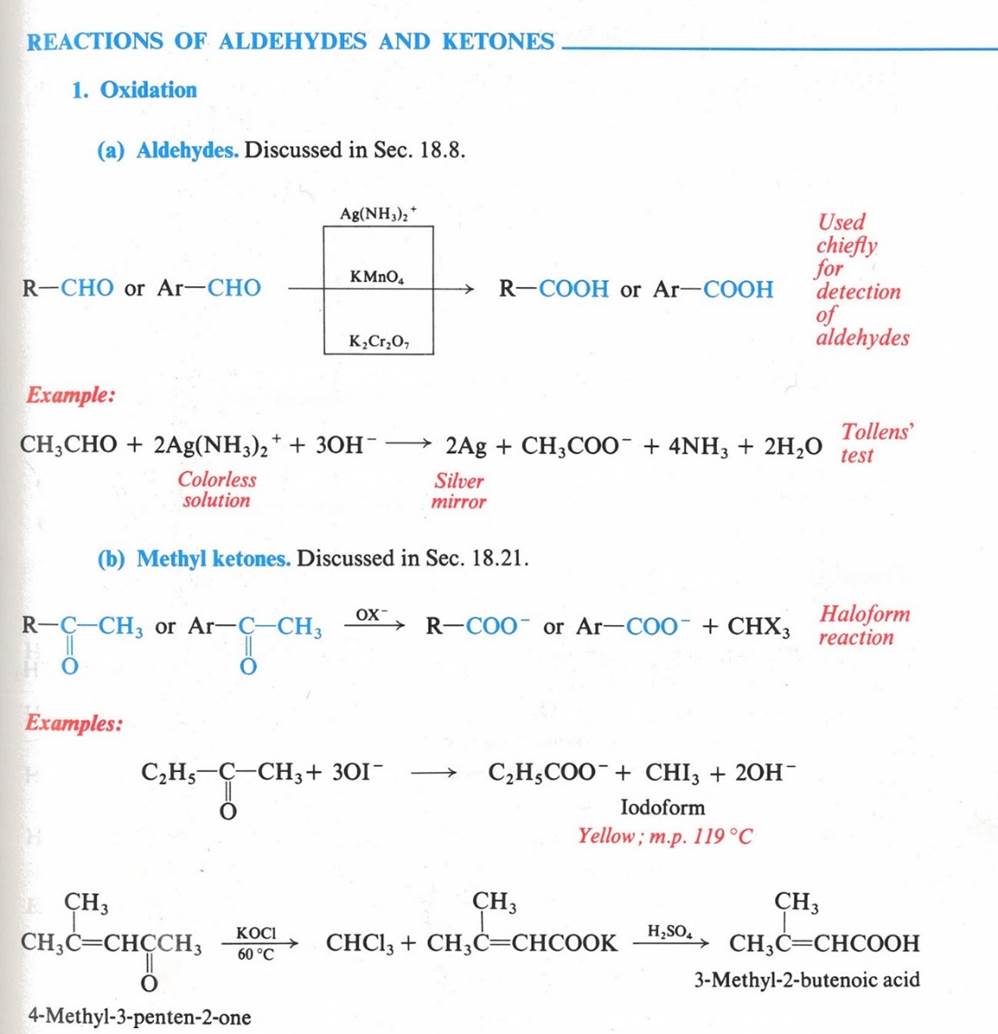
Aldehydes have a hydrogen atom attached to the carbonyl group. This hydrogen affects reactivity in two ways.
a) aldehydes are quite easily oxidized, whereas ketones are oxidized with difficulty
b) aldehydes are usually more reactive than ketones toward nucleophilic addition (the characteristic reaction of carbonyl compounds).
c)
Aldehydes Nomenclature
u Common names
u Derived from the names of corresponding carboxylic acids
u Replace ic with aldehyde
u IUPAC names
u The longest chain carrying the -CHO group is the
parent structure
u Replace -e with -al
Ketones Nomenclature
u Common names
u Derived from the names of the two attached groups to
the carbonyl carbon
u Follow with the name ketone
u IUPAC names
u The longest chain carrying the carbonyl group is the parent structure
u Replace -e with -one
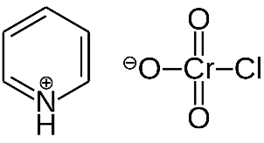
Pyridinium
chlorochromate
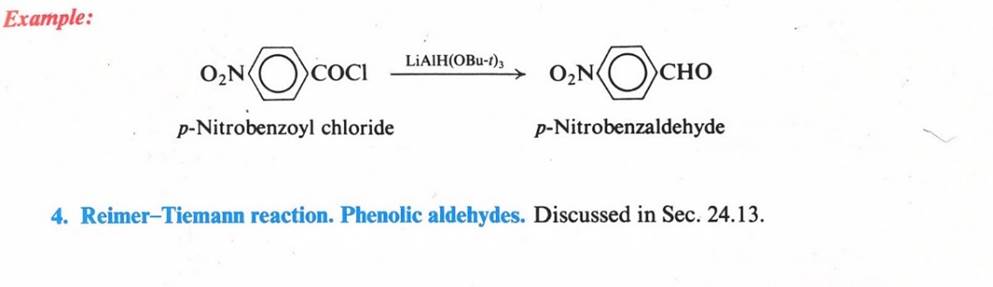
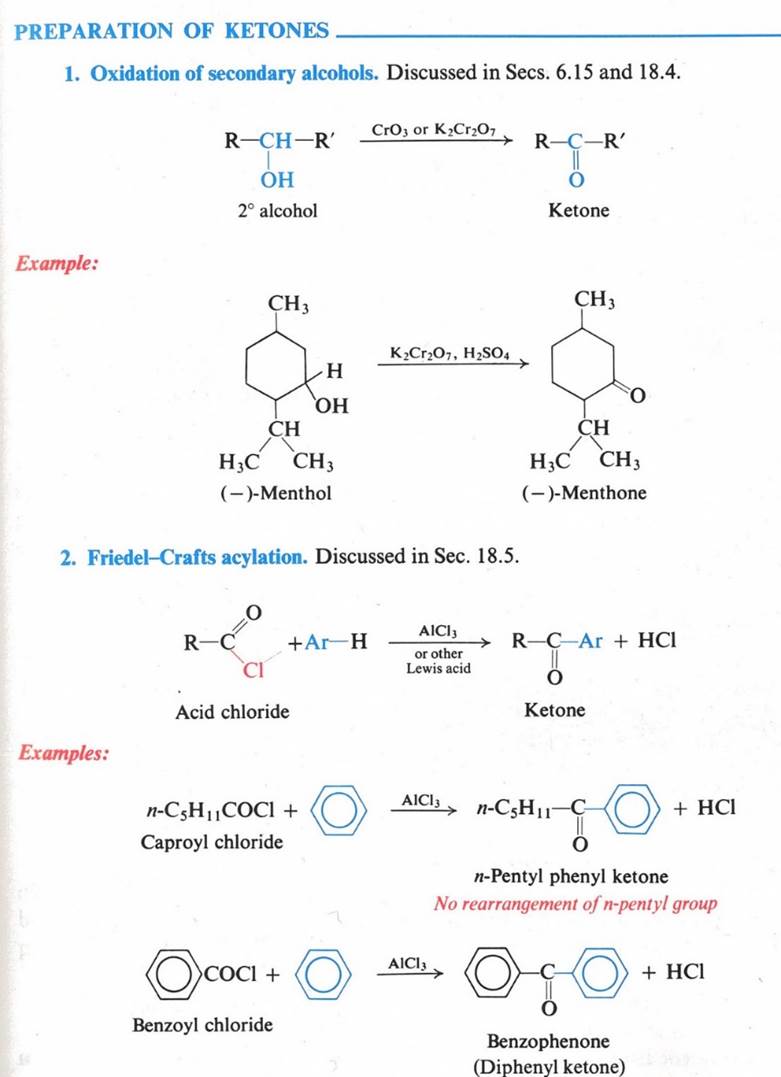
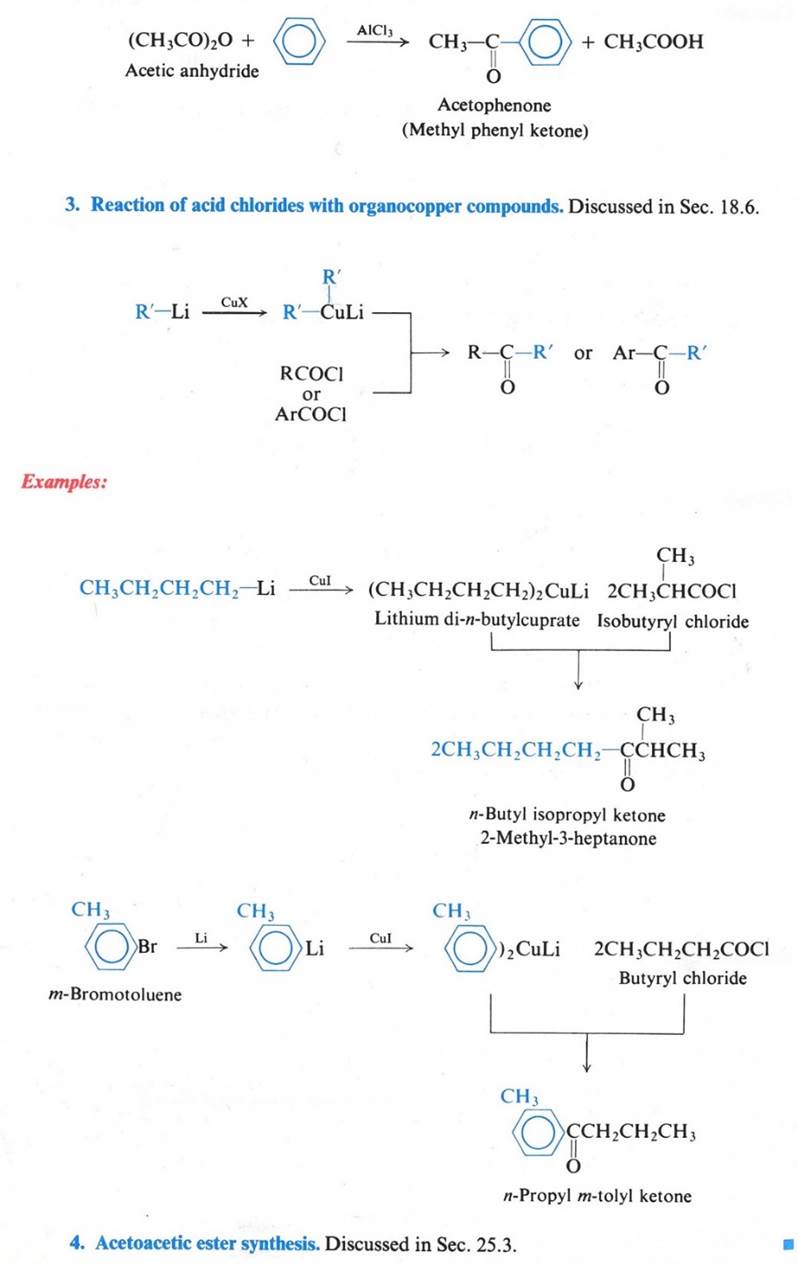
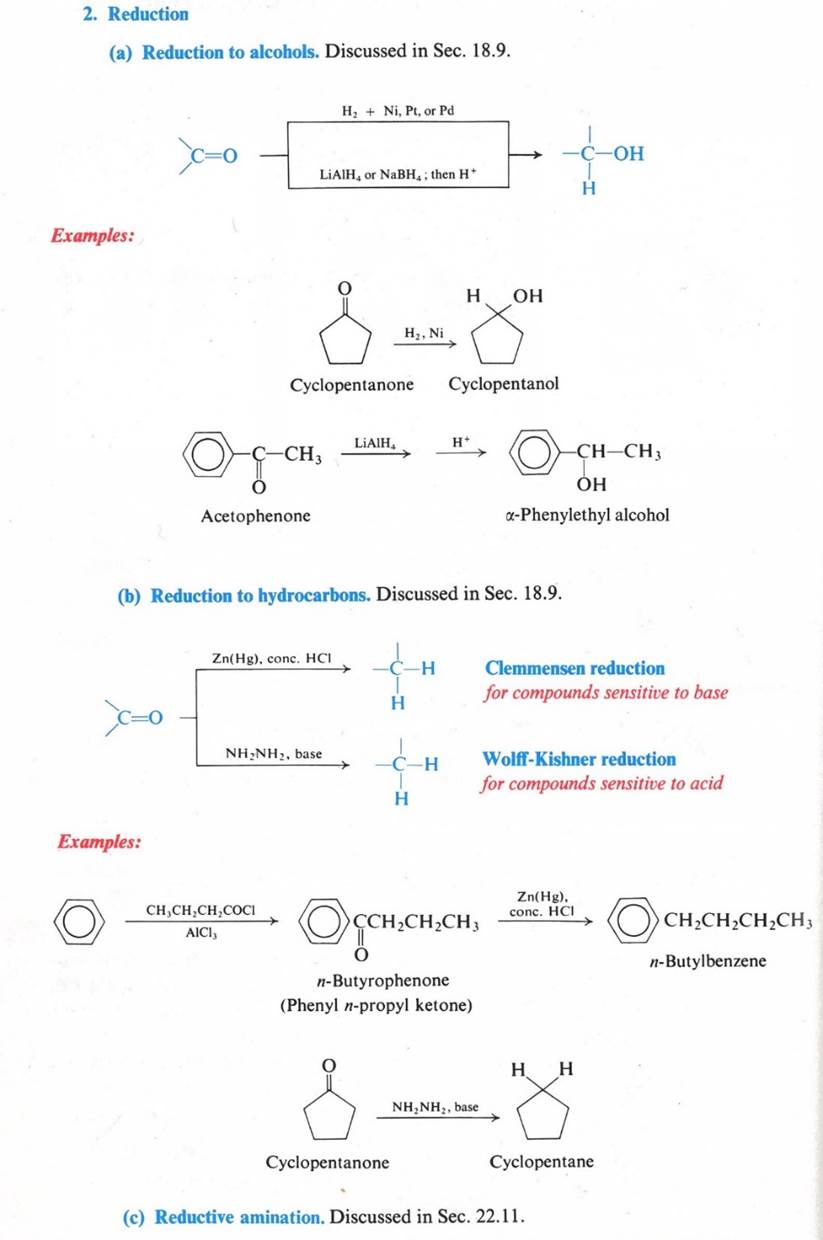
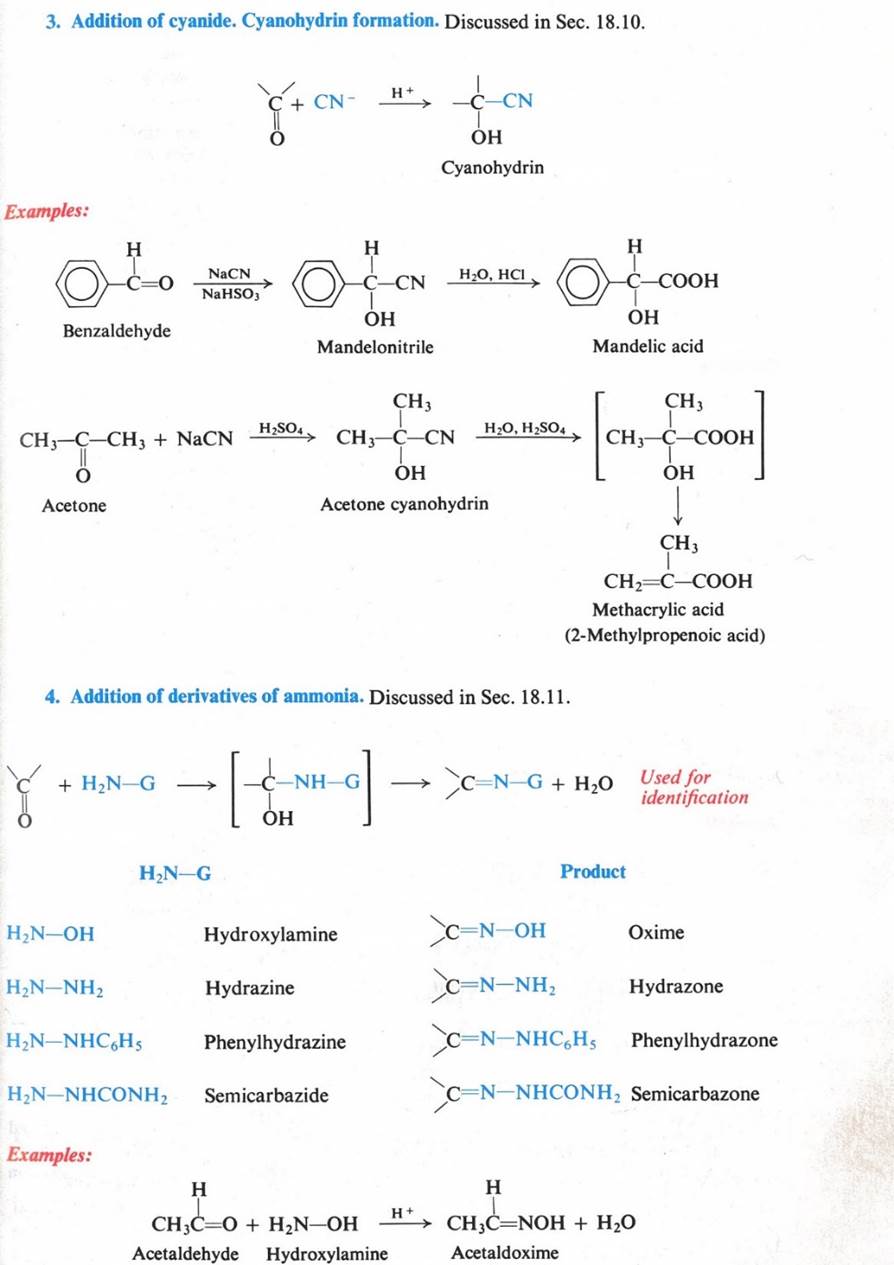
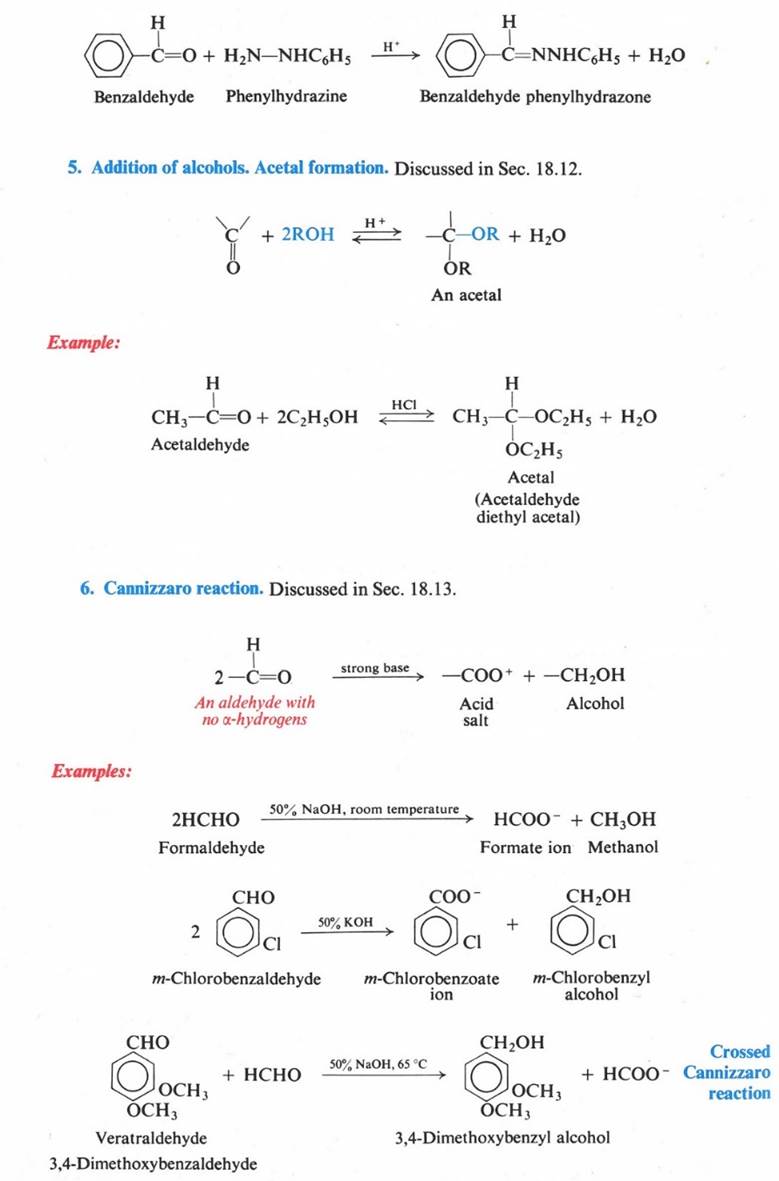
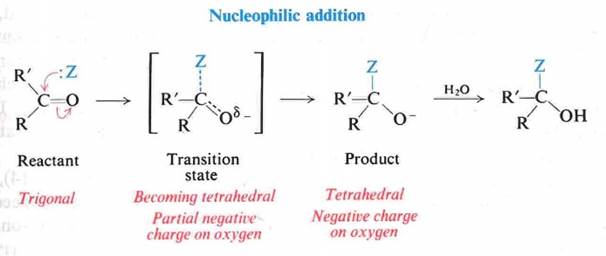
Reactions – Nucleophilic Addition
u The C=O governs the chemistry
u Provides a site for nucleophilic addition
u Increasing acidity of the a hydrogens
u Mobile p electrons are pulled strongly toward oxygen
u Carbonyl carbon – electron-deficient
u Carbonyl oxygen – electron-rich
Acid-catalyzed Nucleophilic Addition
If acid is present, hydrogen
ion becomes attached to the carbonyl oxyge.
Ths prior protonation lowers the Eact for
nucleophilic attack, since it premits oxygen to acquire the p electrons without having to accept a negative
charge. Thus nucleophilic addition to
aldehydes and ketons can be catalyzed by acids (sometimes, by Lewis
acids.)