Generalized Animal Cell
Anatomy
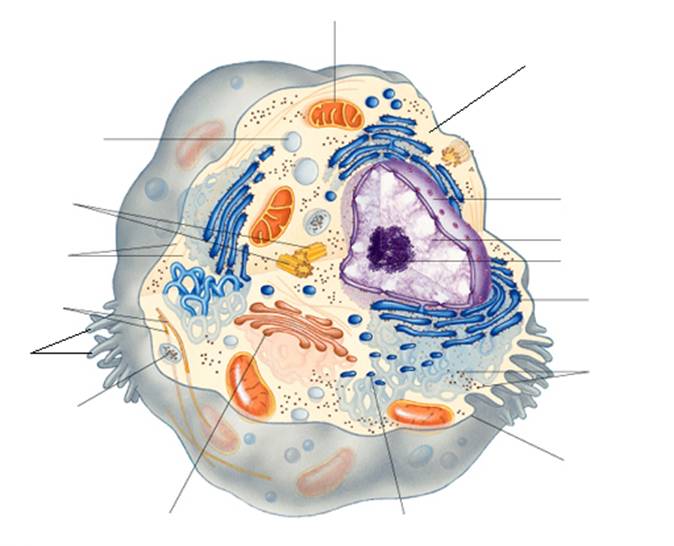
Use the following terms to label the indicated structures within this generalized animal cell.
|
A. |
Centrioles |
G. |
Microtubules |
M. |
Peroxisome |
|
B. |
Chromatin |
H. |
Microvilli |
N. |
Plasma membrane |
|
C. |
Cytoplasm |
I. |
Mitochondria |
O. |
Ribosomes |
|
D. |
Golgi apparatus |
J. |
Nuclear envelope |
P. |
Rough endoplasmic reticulum (ER) |
|
E. |
Lysosome |
K. |
Nucleolus |
Q. |
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum (ER) |
|
F. |
Microfilaments |
L. |
Nucleus |
![]()
Match the following organelles to the description of
their function.
|
___ 1. |
A selectively permeable phospholipid
bilayer that encloses the cytoplasm of a cell. |
A. |
Chromatin |
|
___ 2. |
Microscopic cellular membrane
protrusions that increase the surface area of cells, and are involved in a
wide variety of functions, including absorption, secretion, cellular
adhesion, and transduction. |
B. |
Microvilli |
|
___ 3. |
A membrane-enclosed organelle containing the genetic
information (in the form DNA) of a cell.
It is the “Command Center of the Cell,” responsible for growth and
reproduction. |
C. |
Nuclear envelope |
|
___ 4. |
A darkly staining body within the nucleus of a cell
during interphase.
It plays an important role in ribosome manufacture and, by extension,
protein synthesis. |
D. |
Nucleolus |
|
___ 5. |
Double membrane surrounding the cell nucleus; consists of
outer and inner membranes perforated by nuclear pores. |
E. |
Nucleus |
|
___ 6. |
A complex of DNA, RNA and proteins within the cell
nucleus that will condense to become visible chromosomes during mitosis. |
F. |
Plasma membrane |
Match the following organelles to the description of
their function.
|
___ 7. |
Region of the endoplasmic reticulum that is not studded
with ribosomes and is involved in lipid synthesis. |
A. |
Golgi apparatus |
|
___ 8. |
A system of membranous tubes and sacs containing ribosomes which function in the manufacture of
membrane-bound proteins. |
B. |
Lysosomes |
|
___ 9. |
A protein synthesis 'machine,' made of ribosomal RNAs and
proteins that translates the code on mRNA (messenger
RNA) into proteins. “The Workbench
Upon Which Proteins are Built” |
C. |
Peroxisome |
|
___ 10. |
A series of flattened, membrane-bound sacs involved in
the storage, modification and secretion of proteins and lipids. This organelle packages proteins and
carbohydrates into vesicles for
export from the cell. This organelle
is known as the “Warehouse of the Cell.” |
D. |
Ribosome |
|
___ 11. |
Organelles that contain powerful oxidase
enzymes that use molecular oxygen to detoxify harmful or toxic substances,
such as free radicals and peroxides.
It also participates in the metabolism of fatty acids and other
metabolites. |
E. |
Rough ER |
|
___ 12. |
Organelles that contain digestive enzymes. They digest
excess or worn-out organelles, food particles, and engulfed viruses or
bacteria. Some cell biologists call
these “suicide bags” because they digest cells that are defective. |
F. |
Smooth ER |
Match the following organelles to the description of
their function.
|
___ 13. |
A microscopic network of actin
filaments and microtubules in the cytoplasm that functions as the cell’s
"scaffolding" or "skeleton." It gives the cell its shape and provides
for internal movements and sometimes external movements. |
A. |
Centriole |
|
___ 14. |
Also known as actin filaments,
these are the thinnest filaments of the cytoskeleton. They are usually involved in cell motility
or changes in cell shape. |
B. |
Centrosome |
|
___ 15. |
Components of the cytoskeleton composed of hollow
cylindrical rods, formed of a protein called tubulin. They help cells to maintain their shape;
they also occur in cilia, flagella and the centrioles,
and form the spindle during nuclear division. |
C. |
Cytoskeleton |
|
___ 16. |
One of a pair of small, barrel-shaped microtubule
structures involved in the formation of the spindle during mitosis. |
D. |
Mitochondria |
|
___ 17. |
The area of the cell containing paired centrioles. The centrosome will be replicated during the G2
period of interphase. The centrosomes
move to opposite poles of the cell during prophase, stretching the spindle
fibers between them. Recall that it is
the spindle fibers that move the chromosomes during mitosis. |
E. |
Microfilaments |
|
___ 18. |
An organelle found in the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells
that is responsible for the conversion of food to usable energy in the form
of ATP through a process called cellular
respiration. The inner membrane is folded into pleats called cristae, which
increases the surface area upon which cellular respiration takes place. This organelle contains genetic material
separate from the nucleus called mitochondrial DNA (mDNA). This organelle is known as the “Power House
of the Cell.” |
F. |
Microtubules |