Botany – Plant
Metabolism
I.
Metabolism –
__________________________________________________
A.
______________________ – the
process by which plant cells capture
the radiant energy (E) of sunlight
& store it in sugar (in the form of
carbohydrates).
B.
______________________ – the
process by which plant cells release
the E stored in sugar & capture
it in ATP.
1. ATP – ____________________________________________
II.
Photosynthesis begins with light
A.
What makes up light?
1. Review the diagram over the visible spectrum
of light
2. As wavelength _____________________, energy
_____________________________
a.
Red has the ____________ wavelength, but carries the
________________
energy
b.
Violet has the ___________ wavelength, but carries the
________________
energy
c. UV light carries ___________ energy then
visible light
1) Why is UV light dangerous?
d. Infrared light carries _________ energy than
visible light.
1) This is the same thing as ________
B.
Why do we see colors?
Why are plants green?
Why
should a greenhouse never have green glass?
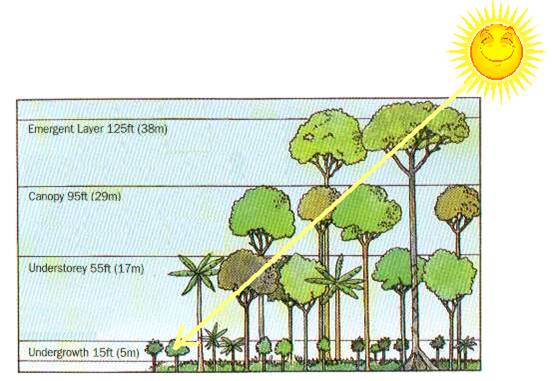
C. Not all light that reaches plants is the
same.
Review how light level changes as you pass through the strata of a
tropical
rain forest.
Images
modified from the following sources: http://homepages.paradise.net.nz/hellyer/images/Rainforeststrata.jpg
http://www.yellowheadcs.ca/images/Sun%20clip%20art.gif
Emergent layer - ______ light
quality; therefore it is the _____ efficient.
These plants primarily
rely upon just have __________________.
Undergrowth - _______ light
quality. Mostly only the high energy
Wavelengths of violet,
blue, and green get through. These
plants
must be the _____
efficient. They primarily rely upon
__________________.
III.
Plants capture the E of light with photosynthetic pigments
A.
Review the diagram over the absorption of the photosynthetic
pigments
1. ________________________,
in land plants, is the main light-
capturing pigment.
a. Chlorophyll a is a _________________________pigment
b. It is most efficient at ___________________________&
_____________________________
wavelengths
2. Chlorophyll b serves as an accessory pigment
a. Chlorophyll b is a _______________________ pigment
b. It is most efficient at __________________________ &
_____________________________wavelengths
3. Chlorophyll transmits & reflects light in
the
_________________________
& ________________________
wavelengths, giving plants their green
color
4. Chlorophyll is located in the __________________________of
chloroplasts
5. __________________________
(carotene & xanthophylls) are
accessory pigments that
allow the utilization of a wider variety of
wavelengths of light.
a. Carotenoids are yellow, orange, or red
pigments
b. They are most efficient at _________________________
& _____________________________
wavelengths
6. Why do shaded plants have more carotenoids?
IV.
Overview of Photosynthesis
A. A SUM OF THE REACTION OF PHOTOSYNTHESIS
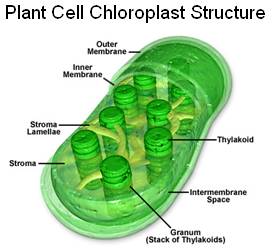
B. Review of the structures of a chloroplast
1. Double membrane bound, stacks of
____________________________ membranes called
____________________________, & a fluid called the
_____________________________.
Image
modified from: http://micro.magnet.fsu.edu/cells/chloroplasts/images/chloroplastsfigure1.jpg
C.
Photosynthesis can be viewed as a coupled oxidation / reduction
reaction
1. Oxidation
– the loss of ___________________________
&/or
_____________________________ (the loss of ______________)
a. water is oxidized as free ________________________ is
created
2. _____________________________
– the gain of electrons &/or
hydrogen (the gain of E)
a. carbon dioxide is reduced as it is changed to
_____________________________
(carbohydrates)
D.
Photosynthetic reactions can be divided into light-dependent &
light-
Independent. THESE REACTIONS BOTH OCCUR IN EVERY SINGLE
PLANT SIMULTANEOUSLY DURING THE DAY.
1. Light-dependent
reactions (require light or they
will not occur)
a. Take place on the ______________________________
b. Water molecules are split (oxidized) to
produce oxygen
and H+
1)
H+ + NADP+ à NADPH
c. The energy of sunlight excites the
photosynthetic
pigments of _____________________________
1) They eject electrons, which travel down the
electron transport system, releasing
energy.
2) Some of the E is used to create a H+
gradient
across
the thylakoid membrane that drives
_____________________________
a) ADP + Pi à ATP
2. Light-independent
reactions (can occur in the dark, don’t
require light)
a. Take place in the _____________________________
b. The energy stored in ATP is used to reduce
carbon
dioxide to
form glucose
1) NADPH donates H to CO2
a) NADPH à NADP+
2) The energy required to reduce CO2
is derived from
ATP
b) ATP à ADP + Pi
3. Overview of Reactants and Products
|
|
Uses (________________________) |
Produces (________________________) |
|
Light-dependent (occurs on thylakoid membranes) |
|
|
|
Light-independent (occurs in the stroma) |
|
|
E.
_____________________________
– a group of protein, chlorophyll,
& carotenoid molecules contained
on the thylakoid membranes. The
photosystems were numbered as they
were discovered, but they are
actually used in reverse order.
1. Photosystem
II
a. A photon of light strikes photosystem II,
energizing an
electron
b. The energized electron moves down the
electron
transport system
1) This E is used to convert ADP + Pi
to ATP
c. The electron is passed to photosystem I
2. Photosystem
I
a. The electron is re-energized by sunlight and
passes to a
carrier
molecule NADP+. H+
from the stroma combines with
electrons to
form NADPH.
b. The NADPH will be utilized in the
light-independent
reactions to
form _____________________________.
3. The original electron from Photosystem II is
replaced by splitting
water.
a. H2O à 2H+ + 2 e- + ½
O2
F. There are 3 types of photosynthesis: __________________________
photosynthesis
1.
Photosynthesis always involves taking C from 6 CO2 and
“_______________” it to form a 6 C
molecule, glucose.
a.
Remember,
plants get CO2 from the air.
They must open
their
somata in order allow CO2 into the leaf’s mesophyll
where
photosynthesis is taking place.
b. When the stomata are open, water vapor leaves
the plant
through
transpiration
2. C3
photosynthesis is the ancestral pathway for carbon fixation
and occurs in all
taxonomic plant groups.
a.
C3
photosynthesis initially fixes CO2 into a 3 C molecule
that
will eventually become glucose.
b.
Benefits
of C3 photosynthesis
i.
_________________________ system (it takes
the
least ATP to make glucose).
c.
Costs of C3 photosynthesis
i.
_______________ must be abundant. In order for
C3
photosynthesis to be efficient, the stomata must
stay
open to let in lots of CO2.
ii.
When
temperatures are high, and water is low, C3
plants
begin to go through photorespiration.
d.
___________________________ consumes oxygen,
releases carbon dioxide, generates
no ATP, and
decreases photosynthetic output.
i.
Generally
occurs on hot, dry, bright days, when
the
stomata close to conserve water.
ii.
This
allows the concentration of O2 to exceed that
of
CO2 in the leaf.
e.
In
C3 plants, the ____________________________ cells
(cells
that surround and protect leaf veins) usually do not
contain
chloroplasts.
f.
Examples
of C3 plants: most trees,
grain crops, potatoes,
sugar
beets.
3. C4
photosynthesis occurs in the more advanced plant taxa and
is
especially common among ______________, such as grasses
and
sedges, but not very common among dicots.
a.
C4
photosynthesis initially fixes CO2 into a 4 C molecule
that
will eventually become glucose.
b.
Benefits
of C4 photosynthesis
i.
At
________________________, C4
plants have
photosynthetic
rates that are two to three times
faster than those of C3
plants.
ii.
C4
plants lose less water during
photosynthesis.
c.
Costs
of C4 photosynthesis
i.
Under
milder climatic conditions, C3 plants are
more
efficient at fixing carbon dioxide.
d.
In
C4 plants, the bundle sheath cells usually do have
chloroplasts.
4. Crassulacean
Acid Metabolism (______________) – usually
found in succulents &
other dry environment plants. The
process
allows C fixation while
maximally conserving H2O.
a. During the day, the light-dependent reactions
produce
ATP & NADPH, but the
____________________________.
C fixation cannot occur.
b. At night, the stomata open, allowing CO2
to enter. Using
CO2 + ATP + NADPH, ________________ is formed.
3. The next day, malate is broken down, freeing
CO2 to
produce ______________.
V.
Glucose metabolism
– how plant cells release & utilize the E stored in sugar
A.
Remember a few things…
1. Cells can’t directly use the E stored in
sugar
2. Cells break the sugar molecule, releasing its
stored E
3. Cells store that released E by making
____________
4. ATP can be used by the cells to do any work
B.
All cells begin the breakdown of sugar through ___________________
1.
Glycolysis occurs in the _______________________ of the cell.
2.
Glycolysis is an anaerobic (not requiring O2) oxidation of
glucose
to produce ____________________________________________.
3. SUM of the formula of GLYCOLYSIS…
Glucose
(a 6 C molecule) à2
Pyruvic acid (a 3 C molecule) + _________
4. If you are a bacteria or yeast cell, this may
be all the E that you
need, but complex plant
& animal cells must be more efficient.
a.
Complex cells use
_____________________________
to
carry out ___________________________________.
C. Review of the structure of a mitochondria
1. Double-membrane bound organelle. The inner membrane is
folded into _________________________.
2. The cristae provide the surface upon which
cellular respiration
occurs.
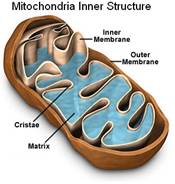
Image modified
from: http://www.cartage.org.lb/en/themes/sciences/zoology/AnimalPhysiology/Anatomy/AnimalCellStructure/Mitochondria/mitochondria.jpg
D.
Cellular respiration –
requires the presences of O2
1. Occurs on the inner membrane of the
mitochondria
2. _______________________________
a. The two pyruvic acids from glycolysis are
converted to
two __________________________ (This is a 2
C sugar)
b. The acetyl groups are caught by a carrier
molecule,
coenzyme A (_____________).
c.
SUM of the TRANSITION STEP
2 Pyruvic acids à 2 CO2 + 2 Acetyl Groups
2 Acetyl Groups + 2 Coenzyme A à 2 Acetyl CoA
d.
The 2 Acetyl CoA enter the _____________________
(also known as the Kreb’s cycle).
3. TCA
Cycle
a. This is a complex chemical reaction that can
be summed
up as
follows…
2 Acetyl CoA à CO2 + H2O + _________________
4.
In conclusion, the YIELD of CELLULAR RESPIRATION can be
summed up in the
following formula…