Botany - Leaves
I. Leaf External Morphology
A. A leaf consists of a
____________________________________ and a
_______________________________________.
1.
The petiole –
2.
The blade –

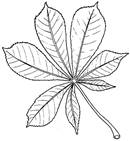
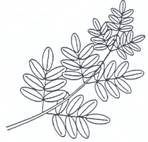
e.g.
Maple tree e.g. Pecan tree e.g. Mimosa or Mesquite trees
3.
Leaves without petioles are called _______________________.
4.
Some leaves have appendages called __________________at
the base of the petiole.
B. ___________________________-
vascular bundles in the blade of the
leaf. Types of venation:
1. _____________________________- large
veins originate at the
base of the blade but run parallel
to each other along the length of
the blade
2.
___________________________- secondary veins branch from
the main vein (midrib)
running along the center of the leaf (dicots)
3.
_____________________________- large veins fan out from the
base of the blade (dicots)
4.
____________________________- small veins fork evenly from
the base of the blade (primitive
trees like Ginkgo)
|
Venation Patterns |
|||
|
______________ |
______________ |
______________ |
______________ |
|
e.g. grass |
e.g. elm trees |
e.g. maple trees |
Ginkgo trees |
C.
Leaf Margins
1. ________________________ – an undivided & unserrated leaf
2. ________________________ - having a notched
or sawlike
edge
3.
________________________ – lobed towards the
midrib but
not reaching it
4.
________________________ –
having a wavy outline or
appearance
5.
________________________ – scalloped or round-toothed
|
Leaf Margins |
|
|||
|
___________ |
_____________ |
____________ |
_____________ |
__________ |
|
e.g. Magnolia tree |
e.g. Elm tree |
e.g. Oak tree |
e.g. Elephant ears |
e.g. Pansies |
D.
Leaves are divided into 2 basic types based upon complexity…
1. Simple
leaves –
2.
Compound leaves- blade is
divided into __________________
on one petiole. There are 3 basic types of compound leaves…
a.
Palmate -
b.
Pinnate -
c.
Bipinnate-
|
Leaf Complexity |
|||
|
|
Compound Leaves |
||
|
Simple |
______________ |
______________ |
______________ |
|
e.g. Maple
tree |
e.g. Blackberries |
e.g. Walnut trees |
e.g. Honey locust, mesquite |
E.
__________________ - arrangement of leaves on the stem.
1. Alternate-
2. Opposite-
3. Whorled-
4. Spiral-
|
Leaf Phyllotaxy |
|||
|
______________ |
______________ |
______________ |
______________ |
|
|
|
|
|
II. Leaf Internal Structure
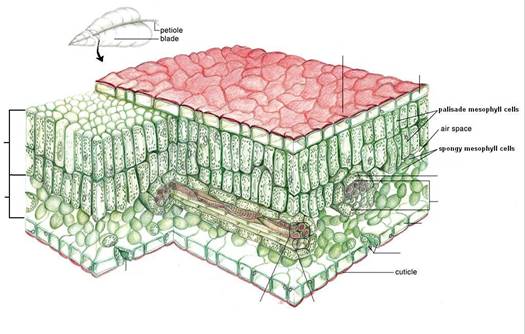
A. Leaves originate as
____________________________________ from
meristematic
tissues.
B. __________________________- the
top and bottom surfaces of a leaf
are covered with epidermis.
1. A __________________________ to prevent water
loss usually
covers the epidermis.
2. Gas exchange occurs
through openings called
_______________________________________
(stoma/stomata).
a. Each
stomata is opened and closed by
______________________________________.
b. Guard cells have chloroplasts.
3. Epidermis may also
contain glands and leaf hairs.
C. ___________________________- the body of the leaf is composed of
mesophyll tissue of two types:
palisade mesophyll and spongy mesophyll
1. The mesophyll carries out
__________________________
2. The mesophyll is composed of chlorenchyma tissue
a. Chlorenchyma tissue
is parenchyma with chloroplasts
3. Most monocots do not differentiate their
mesophyll into spongy
and palisade layers.
D.
__________________________- extensions of the vascular tissue of
the
stem
1.
2.
3.
Vascular bundles are surrounded by the
________________________________
(parenchyma cells)
a.
In C3
plants, the bundle sheath cells usually do not
contain
chloroplasts.
b.
In
C4 plants, the bundle sheath cells usually do have
chloroplasts.
III. Specialized Leaves
A.
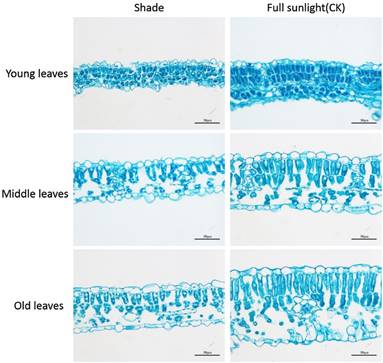
Shade leaves- usually thinner and with fewer leaf
hairs than sun
leaves.
1.
Transverse sections and microscope views of
leaves of 30 days soybean plants grown in shade and
full sunlight (CK). The transverse sections reveal a region between the midvein and the leaf margin. Bars, 50 µm.
Wu, Yushan,
et al. “Shade Inhibits Leaf Size by Controlling Cell Proliferation and
Enlargement in Soybean.” Scientific Reports, vol. 7, no. 1, 2017,
doi:10.1038/s41598-017-10026-5.
B. Arid
regions leaves- in general, plants tend to have the following
characteristics:
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
Succulent leaves—hold water
7.
Hypodermis—
|
|
C. Tendrils- |
|
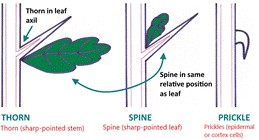
D. Spines,
Thorns, Prickles- 1. Spines
are modified ___________________________ (cactus). 2. Thorns
are modified _________________________(mesquite). 3. Prickles
are modified epidermal or cortex cells (roses, raspberries). Image source: https://www.breamishvalley.com/dog-rose/ |
|
E.
Storage Leaves- succulent leaves
1.
Store water in dry environments
2.
Some are modified for food storage (onions, lilies)
|
|
F. “Flower Pot” leaves- cup-like leaves
found in some species of Dischidia (found in Australia). 1. 2. Illustration of Dischidia major (image credit: wikimedia
commons) |
|
G. Window leaves- buried leaves with a
transparent layer that allows sunlight in. The photosynthetic cells are
buried in the ground. Adaptation to dry, sandy climates. |
|
H.
Reproductive leaves- leaves that can
develop into new plants.
1.
When broken off, they develop into adventitious roots and stems.
|
|
I. Bracts- Photo from aggie-horticulture.tamu.edu |
J.
Insect Trapping Leaves- found on
insectivorous plants, which use
insect
tissues as a source
of _________________________________.
1.
e.g.
|
Carnivorous plant photos provided by Parvinder Kaur, Associate
Prof. In Botany |
||
|
Pitcher
plant |
Sundew
plant |
Venus
flytrap |
|
|
|
|
K. __________________________________
(motor) leaves – Common
in
monocots (especially grasses), bulliform cells are
thin-walled cells on
either
side of the main central vein (midrib).
Under ______________________,
the
bulliform cells partly _____________________. The collapse causes the leaf
to
fold or roll, reducing transpiration.
1.
They also probably play a role in the unfolding of developing
leaves.
Watch this
video of the Fainting Mimosa (also called a Touch-Me-Not plant).
|
IV. Leaf Senescence and Abscission Photo from Pixabay Free for commercial use |
|
A.
____________________________________ - Color Changes
1. Most deciduous trees and
many perennial herbs have leaves
that change from green
to yellow, orange, or red in the fall.
2.
The non-green colors are due to…
a.
Carotenes (________________________________)
b. Xanthophylls
(________________________________)
c. Anthocyanins
(______________________________) and
d. Betacyanins
(________________________________).
3. These pigments are always present
but are masked by
________________________________.
a.
B.
____________________________________- dropping of leaves
1. Occurs at the abscission
cells zone near the base of each
petiole.
2.
Hormones
inhibit the formation of abscission cells during the
growth of young leaves.
3.
As the leaf ages, hormonal changes occur, and at least two
layers of cells differentiate into the
___________________________________and
the
____________________________________.
a.
The
protective layer is several cells
deep and highly
suberized.
1)
It
protects the rest if the plant from invasion and
water loss when the leaf drops.
b.
The
separation layer contains cells that
produce a lot of
pectin.
4.
Certain environmental cues (temperature, day length) cause the
activation of enzymes that degrade
the pectin, causing the lamellae
to separate.
a.
A few strands of xylem still hold the leaf, but wind or rain
easily breaks them.
5. ________________________________-
drop leaves seasonally
6.
__________________________________ also drop leaves, but
not all at once.