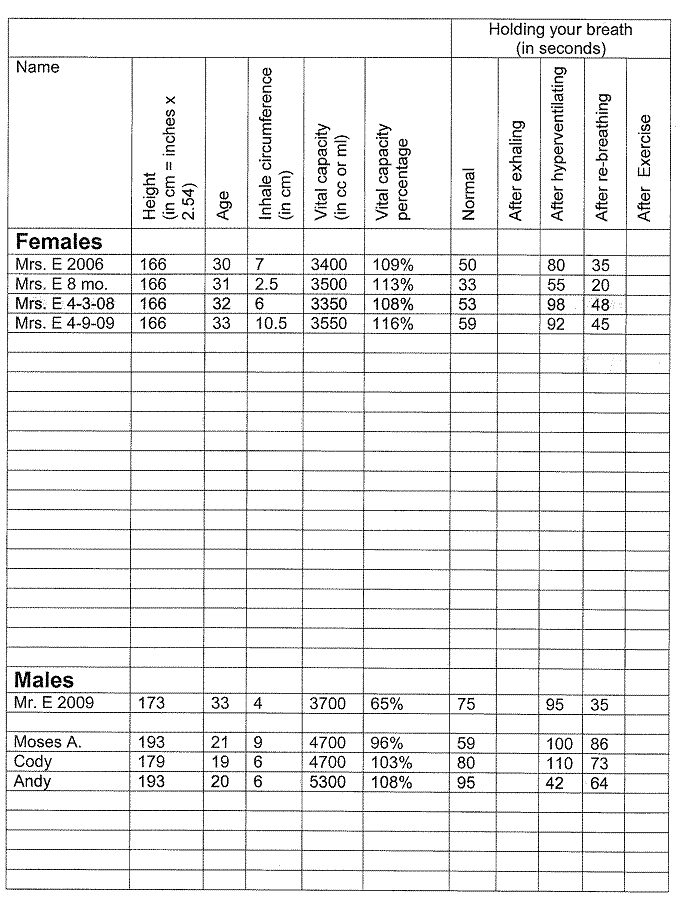
Name:
__________________________
Human A&P II: Respiratory System Physiology
Review the
following terms: ventilation,
inspiration, expiration, spirometer,
Complete the
table below by filling out the missing terms and volumes:
|
Term |
Abbreviation |
Definition |
Volume (in ml) |
|
|
TV |
Amount of
air inhaled or exhaled with each breath under resting conditions |
|
|
|
IRV |
Amount of
air that can be forcefully inhaled after a normal tidal volume inhalation |
|
|
|
ERV |
Amount of
air that can be forcefully exhaled after a normal tidal volume exhalation |
|
|
|
VC |
Maximum
amount of air that can be exhaled after a maximal inspiration |
|
Complete the
following exercises…
- Have your partner count your normal
respiratory rate: Respirations per
minute = ________
- The average is 12 breaths per
minute
- Assuming that your tidal volume
is average (500ml), what is your minute respiratory volume (MRV)?
- MRV = TV x respirations/minute =
500ml x ____ = ______ml/min
- Use the measuring tape to record
how many inches you can expand your ribcage. Wrap measuring tape just below your
breasts and pull it snug during an exhalation. Then strain to inhale as much as
possible. How many inches have your
ribs expanded?
Measurement
before inhaling: _______cm Measurement after inhaling: _______cm
- How long can you hold your
breath? (You’ll need a timer for
this exercise.)
- Have your subject breathe normally for 2 minutes,
then inhale deeply and hold his or her breath for as long as he or she
can.
i. After breathing normally, held breath
for _______ sec.
ii. Did the subject fill the urge to
inhale or exhale during breath holding? _______
- Have the subject breathe
normally for another 2 minutes, then inhale deeply, but now exhale completely and forcefully
before holding his/her breath for as long he/she can.
i. After exhaling, held breath for
_______ sec.
ii. Did the subject fill the urge to
inhale or exhale during breath holding? _______
- Have the subject hyperventilate (breathe deeply
& forcefully at the rate of 1 breath/4 sec) for about 30 seconds (a
sensation of dizziness may develop).
Have the subject hold his or her breath for as long as he or she
can.
i. After hyperventilating, held breath
for _______ sec.
ii. Was this longer or shorter than the
first time? ____________
- Have the subject re-breathe (breathe into a paper
bag) for 3 minutes, then hold his/her breath for as long as he/she can.
i. After re-breathing, held breath for
_______ sec.
ii. Was this longer or shorter than the
first time? ____________
- Have the subject run in place for 2 minutes and
then hold his/her breath for as long as he/she can.
i. After exercising, held breath for
_______ sec.
ii. Was this longer or shorter than the
first time? ____________
- Use
the spirometer
to measure the following…
- Expiratory
reserve volume (ERV)
– inhale and exhale normally 2 or 3 times, then insert the spirometer
mouthpiece and exhale forcibly as much of the additional air as you
can. Record your results below.
i. Trial 1 ERV = _______ml iii. Trial 3 ERV = _______ml
ii. Trial 2 ERV = _______ml iv. Average ERV = _______ml
1. Average ERV ranges from 1,000 to
1,200ml
- Vital
Capacity (VC) –
breathe in and out normally 2 or 3 times, and then bend over and exhale
all the air possible. Then, as you
raise yourself to the upright position, inhale as fully as possible. (It is very important to strain to inhale the maximum
amount of air that you can.)
Quickly insert the mouthpiece, and exhale as forcibly as you
can. Record your results below.
i. Trial 1 VC = _______ml iii. Trial 3 VC = _______ml
ii. Trial 2 VC = _______ml iv. Average VC = _______ml
1. Average VC is about 4,500ml, ranging
from 3,600 to 4,800ml
- How closely does your vital
capacity volume compare to the predicted
values for someone your age, sex, and height. (Obtain this figure from a table.) Notice that you will have to convert
your height in inches to centimeters (cm) to find the corresponding value.
- Height in cm = height in inches
x 2.54 = ________ cm
- Predicted VC value (from the
table) = ________ml
- Compare your VC to the predicted
VC using the following formula:
i. %
of predicted VC = Average
measured VC x 100 = _____%
Predicted
VC
- Calculate
your Inspiratory Reserve Volume (IRV)
- IRV = VC – (TV + ERV)
- IRV = _________ - (500 + _____ )
= ___________ml
- Average IRV range from 2,100ml
to 3,100ml
- Calculate
your Residual Volume (RV)
- RV = VC x factor = ________ml
i. Factor for ages 16-34 = 0.250
ii. Factor for ages 35-49 = 0.305
iii. Factor for ages 50-69 = 0.445
iv. Average RV is 1,200ml