ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
I.
Introduction to Endocrine system
A.
Endocrine glands - ductless glands, epithelial cells specialized for
synthesis
and secretion of hormones
B.
________________________________ – chemical messengers released
into the bloodstream &
transported a distance from the endocrine organ to a
target cell or tissue.
C.
Involved in controlling ___________________________________________
of cells; regulate, direct and
control long term changes
D.
Target cells must have cell-surface receptors capable of binding hormone
to
cause effect
1.
Response
of target cell can occur within minutes to hours, depending
2.
upon
the type of hormone
II.
The chemistry of hormones
A.
Nearly all can be classified into two types based upon structure
1. ________________________________ – synthesized
from cholesterol
a. ex)
estrogen, testosterone, progesterone, corticoids
2. _______________________________________ (or
water-soluble) –
most common type of
hormone
a.
many are derived from amino acids
b.
ex) amines (dopamine, histamine,
serotonin, epinephrine),
thyroxine,
peptides (insulin, growth hormone)
3. ________________________________ – a small 3rd
class
a.
include leukotrienes (mediate inflammation) & prostaglandins
(raise
BP, increase uterine contractions during labor)
III.
Mechanisms of hormone action
A.
Hormones work by altering cell activity, either increasing or decreasing
rates
of normal cellular activities, the
specific response depends upon the target cell
B. Hormonal stimulus usually produces one or
more of the following
1. Alters cell membrane permeability or membrane
potential or both
2. Stimulates synthesis of proteins or
regulatory molecules such as
enzymes
3. Activates or deactivates enzymes
4. Induces secretory activity
5. Stimulates mitosis or cell division
C. Nearly all amino acid-based hormones exert
their effects through an
intracellular
messenger that is activated when a hormone binds to a membrane
receptor
D.
Steroid hormones are lipid soluble & diffuse into the cell, where
they bind to
intracellular receptors, migrate to
the nucleus, and activate specific target
sequences of
________________________________
IV.
Control of hormone release
A.
Synthesis & release of most hormones is controlled by negative feedback
system
B.
Major endocrine glands are stimulated to make & release hormones by
3
types of stimuli…
1. ________________________________ stimuli –
some endocrine
glands secrete hormones in
response to changing blood levels of ions &
nutrients
a. ex) Parathyroid gland monitors [Ca+2]
levels in blood & secretes
parathyroid
hormone (PTH) in response to lowered Ca+2 levels
2. ________________________________ stimuli –
nerve fibers stimulate
hormone release
a. ex)
Sympathetic nervous system stimulation of adrenal medulla
to release
epinephrine and norepinephrine
b.
hypothalamus: links autonomic N.S. and endocrine systems
1)
regulates: response to stimuli, hunger, thirst, sleep, body
temperature,
wakefulness, sex drive, menstrual cycle,
pituitary
gland
2) releasing or inhibiting hormones to anterior
pituitary
3)
ex) Oxytocin & antidiuretic hormone (ADH) release from
posterior
pituitary gland due to hypothalamic neuron
impulses
3. ________________________________ stimuli –
endocrine glands
release hormones in
response to hormones of other endocrine glands
a. ex)
Release of anterior pituitary hormones controlled by
releasing
& inhibiting hormones produced by hypothalamus
b. ex)
Anterior pituitary hormones stimulate other endocrine organs
V. Major endocrine glands
A.
The
________________________________ (hypophysis) - regulates other
B.
endocrine glands and some body activities
1. Located at base of brain in sella turcica of
sphenoid bone
2. Major endocrine gland; secretes at least 9
major hormones
3. An extension of the hypothalamus via the
pituitary stalk or infundibulum
4. In humans, contains two major lobes: anterior (75%) & posterior (25%)
B.
The ________________________________gland (adenophypophysis)
1. ________________________________ hormone (GH)
a.
Stimulates most body cells to increase in size & divide
b.
Stimulates epiphyseal plate to cause long bone growth
c. Promotes
increased muscle mass in skeletal muscles (potential
for abuse?)
2. ________________________________ hormone (TSH) – a.k.a.
thyrotropin
a.
Stimulates development & secretory activity of thyroid hormone
b. Release
of TSH stimulated by thyrotropin-releasing hormone
(TRH)
1)
Release stimulated by cold temperatures & stress
3. ________________________________ hormone (ACTH)
a.
Stimulates adrenal cortex to release corticosteroid hormones
(e.g. glucocorticoids)
b. Release
stimulated by stress, fever, hypoglycemia
4. Gonadotropins
– FSH & LH – stimulates gamete production, turned
on at puberty
a.
________________________________ hormone
(FSH)
1)
promotes ovarian follicle development (to produce eggs)
in
ovary
2)
regulates sperm cell production in testes
b.
________________________________ hormone
(LH)
1)
promotes ovulation & ovarian hormone secretion
2)
promotes production of androgens in males
5. ________________________________ (PRL)
a.
Stimulates mammary gland development & milk production in
females
b. May play
a role in enhancing testosterone production in males
6. Pro-opiomelanocortin
(POMC) – a prohomone that is the source of
adrenocorticotropic hormone
& two opiates
C.
________________________________ Gland (neurohypophysis)
1. Hormones are produced by hypothalamic
neurons, travel via axons to
the posterior pituitary,
& are stored in vesicles until released into the blood
by nerve impulse signal
2. _____________________________ – (positive
feedback mechanism)
a.
acts on smooth muscle of the uterus & breast to cause uterine
contractions
during childbirth & milk let-down during nursing
3. ________________________________ hormone (ADH) – a.k.a.
vasopressin
a. peptide
hormone that acts on kidney tubules to promote
increased
water reabsorption (to decrease urine output)
b. release
promoted by pain, low BP, certain drugs such as nicotine
&
barbiturates
c. alcohol
consumption inhibits ADH secretion àcopious urine
output
D. ________________________________ gland: the
only gland to produce and
store
large amounts of hormones
1. Located below larynx & surrounds the
trachea
a.
consists of hollow follicles with follicle cells that produce
thyroglobin
1)
thyroglobin – storage, iodine attached to amino acid
tyrosine
b.
also consists of parafollicular cells that produce calcitonin
2. Thyroid hormone consists of two amine hormones
– derived from
thyroglobin
a.
________________________________ (T4) &
________________________________
(T3) – refers to 4 or 3
iodine
atoms
bound to protein. T4 is
converted to T3 in the blood
b.
stimulates enzymes concerned with glucose oxidation
àincreases basal metabolic rate &
oxygen consumption as well as
heat
production
3. ________________________________ – a peptide
hormone that
lowers blood calcium
& phosphate levels by inhibiting osteoclasts &
stimulating osteoblasts àbone formation
a. more
important during childhood, when skeleton grows rapidly
E.
________________________________ glands:
Four small glands on
posterior surface of thyroid gland
1. Parathyroid
hormone (PTH) – increases blood calcium levels &
lowers phosphate levels
at the kidney
a.
stimulates osteoclasts, enhances resorption of calcium by
kidneys
& increases absorption of calcium by intestinal epithelial
cells
1)
vitamin D is necessary for absorption of calcium from food
F.
________________________________ (suprarenal) glands: consists of 2
regions, an inner adrenal medulla
& an outer adrenal cortex
1. Adrenal
cortex: secretes hormones from three distinct regions
a. zona
glomerulosa: secretes mineralocorticoids,
chiefly
________________________________
1)
control the [electrolytes] in blood; primarily sodium &
potassium
2)
aldosterone reduces excretion of sodium from body
3)
secretion is stimulated by rising blood [potassium], low
[sodium],
decreasing blood volume & blood pressure
4)
secretion is also regulated by rennin-angiotensisn
mechanism
& secretion of ACTH
b. zona
fasciculata: secretes
_____________________________
1)
influence metabolism of body cells; help us resist
stressors;
anti-inflammatory
2)
help keep blood [glucose] level, maintain blood volume
3)
glucocorticoids include cortisol, cortisone, corticosterone
c. zonal
reticularis: secretes gonadocorticoids,
mostly weak
androgens,
which are converted to testosterone and estrogens in
the tissue
cells
1)
contribute to onset of puberty & body hair production
2)
output in females is higher than males
3)
in females, thought to be involved in sex drive
2. Adrenal medulla: also controlled by
sympathetic NS
a.
________________________________: elevates blood-glucose
levels,
raises blood pressure, heart rate, liver breakdown of
glycogen to
glucose, breakdown triglycerides
b. ________________________________:
increases heart rate,
force of
heart muscle, blood vessels constrict, breakdown
triglycerides
c.
"fight or flight" may be caused by emotions, injury, exercise, low
blood-glucose
levels
G.
________________________________: located behind stomach; composed
of endocrine and exocrine cells
1. Islets of Langerhans cells
secrete 4 different molecules
a. alpha cells secrete
________________________________
during times
of low blood sugar, also triggered by sympathetic NS
and
epinephrine (Glucagon is released when sugar is gone.)
1)
protein hormone that causes liver to convert glycogen to
glucose
which is released to the bloodstream àelevates
blood
glucose levels
2)
also promotes gluconeogenesis (use of non-carbohydrate
precursors
to make glucose)
b. beta cells secrete
________________________________
during fed
states, triggered by high blood glucose level, intestinal
hormones
& parasympathetic nervous activity
1)
protein hormone that lowers blood glucose levels by
enhancing
transport of glucose into body cells, especially
muscle
& fat cells
2)
inhibits gluconeogenesis & catabolism of fats or amino
acids
to glucose
3)
promotes synthesis of glycogen, triglycerides, & protein
c. delta cells secrete somatostatin
1)
hormone that regulates levels of insulin & glucagons by
inhibiting
synthesis of both
2)
also inhibits all parts of the digestive system
d. F-cells secrete pancreatic polypeptide
1)
inhibits somatostatin synthesis & pancreatic enzyme
secretion
2. Exocrine part of pancreas secretes pancreatic
enzymes (used in food
digestion)
H.
Gonads
1. Ovaries produce estrogens & progesterone
a.
estradiol: female characteristics, sex organs
b.
relaxin: regulates pregnancy
2. Testes produce testosterone: male
characteristics, develop sex organs
a.
inhibin: inhibits FSH secretion at anterior pituitary
I.
________________________________ gland: located between cerebral
hemispheres in thalamus, connected to
optic nerve & hypothalamus
1. Produces ________________________________;
lack of light (hours
of
dark) converts this to ________________________________
a.
peak levels of melatonin occur during night & make us drowsy
b.
more melatonin is produced in the winter season
1)
SAD – seasonal affective disorder:
winter depression
more
common in females; due to high melatonin levels;
treatment
involves use of bright light therapy (3-6 hours)
c.
circadian rhythm: 24-hour day and night cycle; determines sleep
vs.
wake cycles in other animals
J.
The thymus gland: in mediastinum anterior to heart
1. Much larger in children; shrinks in size in
adult
2. Produces thymosin,
a mixture of three hormones that are essential for
normal
development of T lymphocytes (T cells) and the immune response
VI. Other hormone-producing structures
A.
Heart secretes atrial natriureptic peptide (ANP)
1. Inhibits secreation of ADH, aldosterone, and
stimulates urine
production
a. results
in decreased blood volume, blood pressure, & blood
sodium
concentration
B.
Stomach secretes gastrin, which turns on gastric glands
1. Somatostatin inhibits acid secretion and
stomach activity
C.
Small intestine
1. Secretin: turns on liver/pancreas bicarbonate
ion secretion & inhibits
gastric glands
2. Cholecystokinin:
turns on pancreatic enzymes, release of bile from
gallbladder, &
inhibits gastric glands
D.
Placenta
1. Secretes estrogens & progesterones
2. Secretes human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG):
maintains corpus
luteum for embryo
implantation and initial growth
E.
Kidney
1. Produces ________________________________, signaling
bone
marrow to increase RBC
production
2. Also produces calcitrol, which eventually
forms vitamin D which acts as
a hormone to stimulate
calcium uptake by bones
3. ________________________________: sodium and
water retention
F.
Adipose tissue
1. Release leptin hormone, which binds to CNS
neurons to produce a
sensation of satiety
(suppress apetite)
VII. Homeostatic imbalances of the endocrine
system
|
Disorders of Growth Hormone |
|
|
Gigantism |
Acromegaly |
|
|
|
|
Progeria |
Pituitary
Dwarfism |
|
|
|
A.
________________________________: hypersecretion of GH in children
àabnormally tall (8 feet) w/relatively
normal body proportions
B.
________________________________: “enlarged extremities”: excessive
GH after epiphyseal plates are
closed. Overgrowth of bones still
responsive to
GH àhands, feet, & face. Enlarged tongue. Usually due to adenohypophyseal
tumor, treated by surgical removal
C.
Progeria: hyposecretion of GH in adults.
Rarely causes problems, but if
severe, body tissues begin to
atrophy & clinical signs of premature aging appear.
D.
______________________________________________: GH deficiency in
children, slowed bone growth (4 feet
tall), fairly normal body proportions.
1. If TSH & gonadotropins are lacking,
malproportioned & fail to mature
sexually
E.
__________________________________________: deficiency of ADH –
marked by output of huge amounts of
urine (polyuria) & intense thirst.
Can be
caused by blow to head, damaging
hypothalamus or the posterior pituitary.
Not
serious as long as you drink enough.
|
Disorders of Thyroid Hormones |
||
|
Hyperthyroidism |
Hypothyroidism |
|
|
|
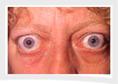
Characteristic bulging eyes |
|
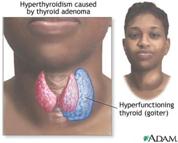
F. ________________________________: increased T4
and T3. Excessive
metabolic
rate. Bulging eyes. Increase hunger & food intake, but
decreased
weight. Bones weaken & body muscles atrophy. Skin is thin, flushed, & moist.
1.
________________________________ in adults – most common
hyperthyroid
pathology
G.
________________________________: decreased T4 and T3. Slowed
metabolism, obesity, diminished
thought processes, lethargy. Skin pale,
thick, &
dry.
They feel chilled, constipated.
1. Myxedema in adults
2. Cretinism in infants àshort, tongue & neck thick,
mentally retarded
H.
Hyperparathyroidism: rare, usually due to parathyroid gland tumor. Ca++ is
leached from bones, which soften &
deform as fibrous connective tissue replaces
mineral salts.
1. Increased Ca++ in blood leads to
depression of NS reflexes &
weakness,
also kidney stones
I.
Hypoparathyroidism: PTH deficiency.
Parathyroid trauma or surgical removal.
1. Hypocalcemia – increased excitability of
neurons
2. Tetany – loss of sensation, muscle twitches,
& convulsions
J.
Aldosteronism: increase in aldosterone due to adrenal neoplasms
1. Hypertension & edema due to excessive
sodium & water retention
2. Accelerated excretion of potassium ions àneurons become
nonresponsive
& muscle weakens
K. ________________________________:
hyposecretion of the adrenal cortex,
decreased
mineralocorticoids & glucocorticoids.
1. Lose weight; decreased plasma glucose &
sodium; increased
potassium.
2. Severe dehydration & hypotension.
|
Cushing’s Disease |
|
|
|
|
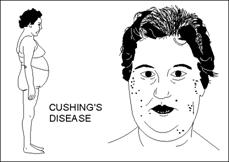
L.
________________________________________ or syndrome: increase in
cortisone. Hyperglycemia, losses in muscle & bone
protein. Water & salt
retention àhypertension & edema. Redistribution of fat to abdomen &
posterior
neck.
Tendency to bruise & poor wound healing. Anti-inflammatory effects
àcan lead to overwhelming infection
before symptoms develop.
M.
_____________________________________________:
blood sugar levels stay high.
1. Sugars aren’t used as cellular fuel. Fats are mobilized, fatty acids
accumulate in
blood,decreasing blood pH àketoacidosis
a.
rapid deep breathing to blow off carbon dioxide, disrupts heart
and
oxygen transportation. Severe depression
of NS leads to
coma
& death
b.
3 cardinal signs
1)
________________________________ – increased urine
output
2)
________________________________ – thirst
3)
________________________________ – excessive
Hunger
2. Type I Diabetes (juvenile onset) - decrease
in insulin production. Often
caused
by an autoimmune attack of the Islets of Langerhans cells of the
pancreas
3. Type II Diabetes (adult onset) – insulin
levels may be produced in
normal
amounts, but the cells have become resistant to the effects of
the
insulin
a. Risk factors – diets high in simple sugars,
lack of exercise,
&
excessive weights